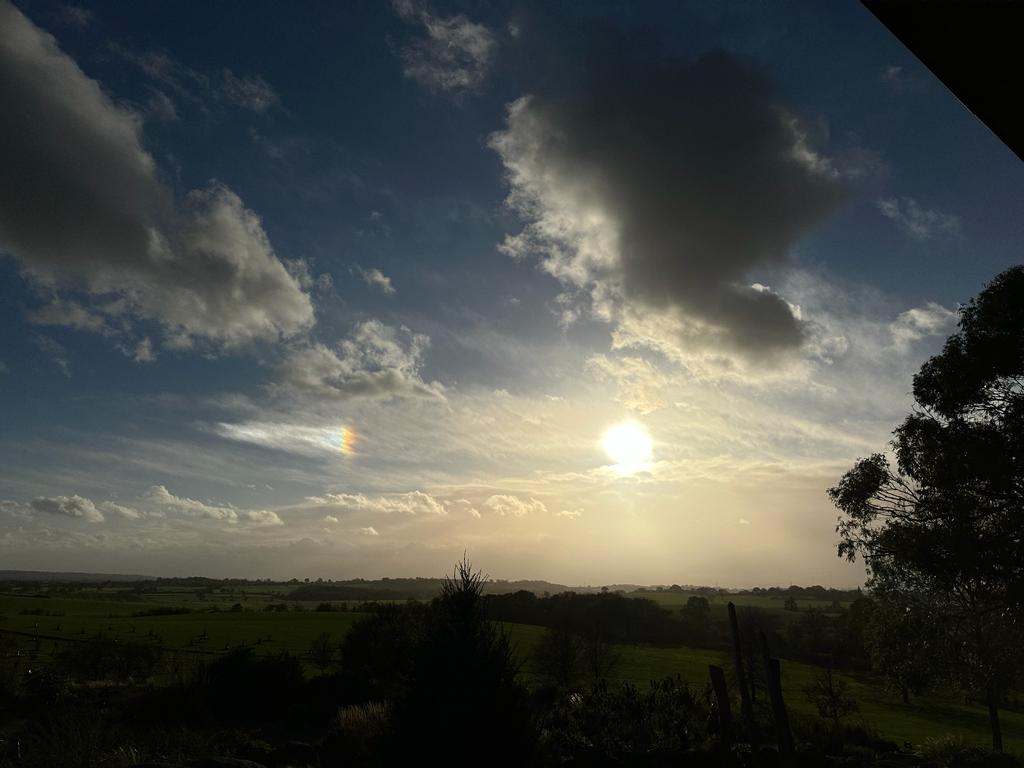
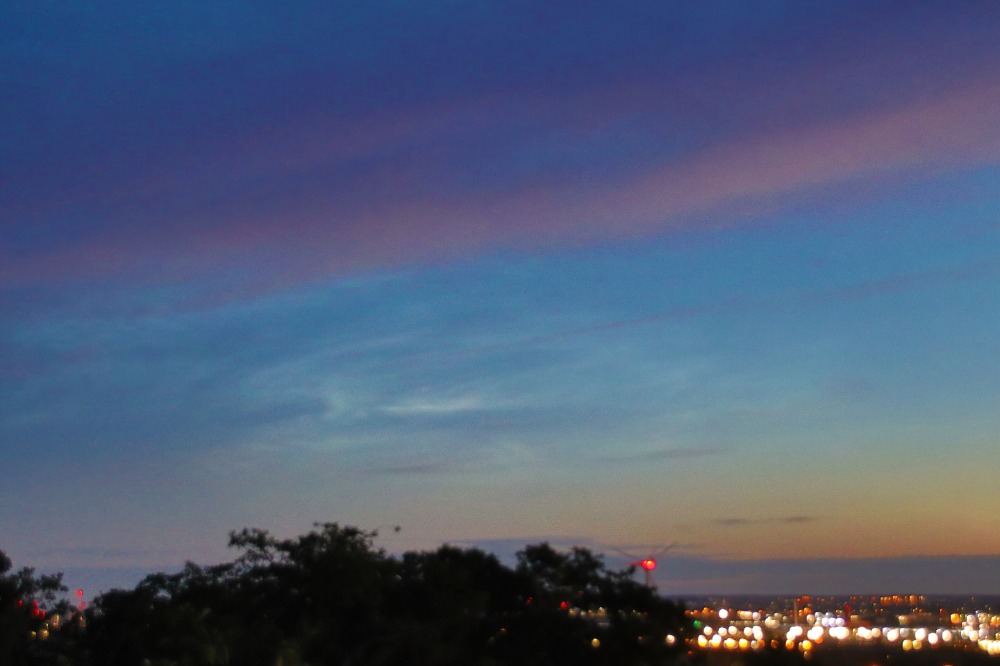
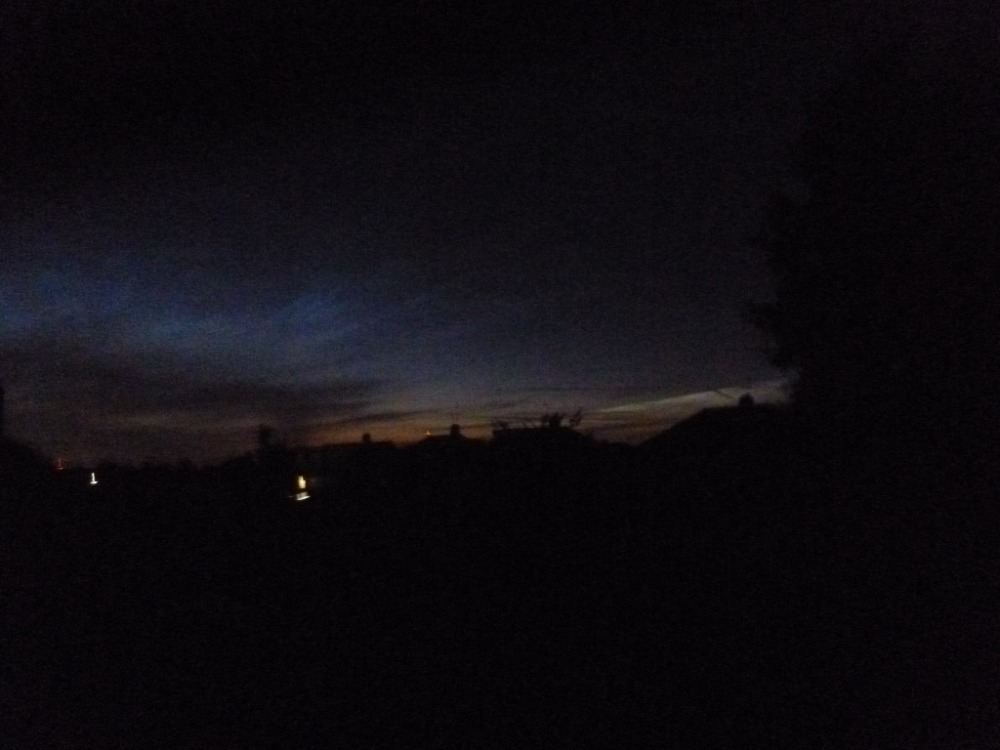
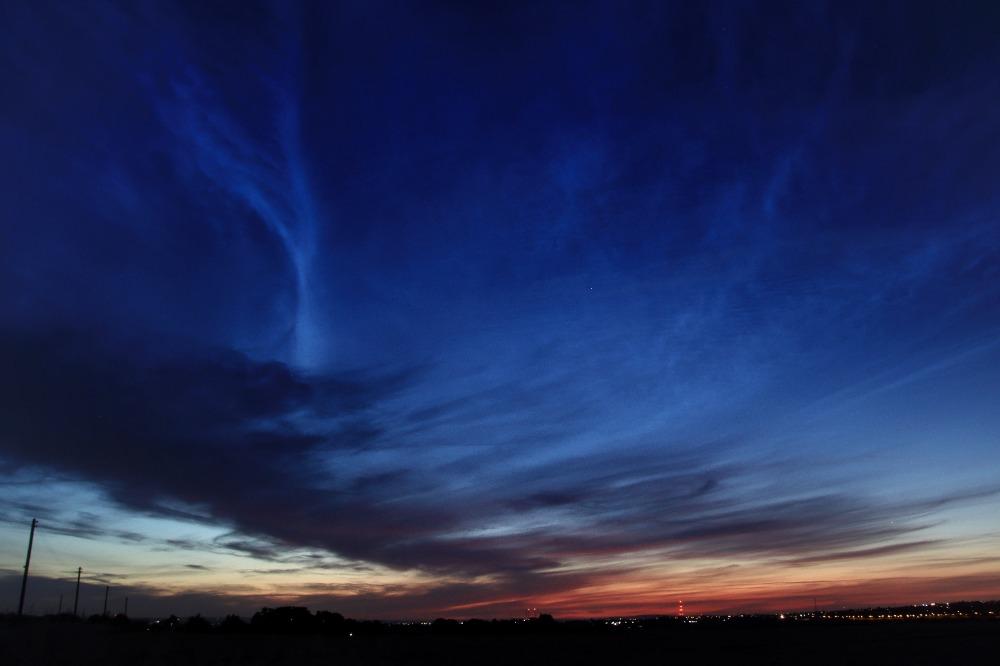
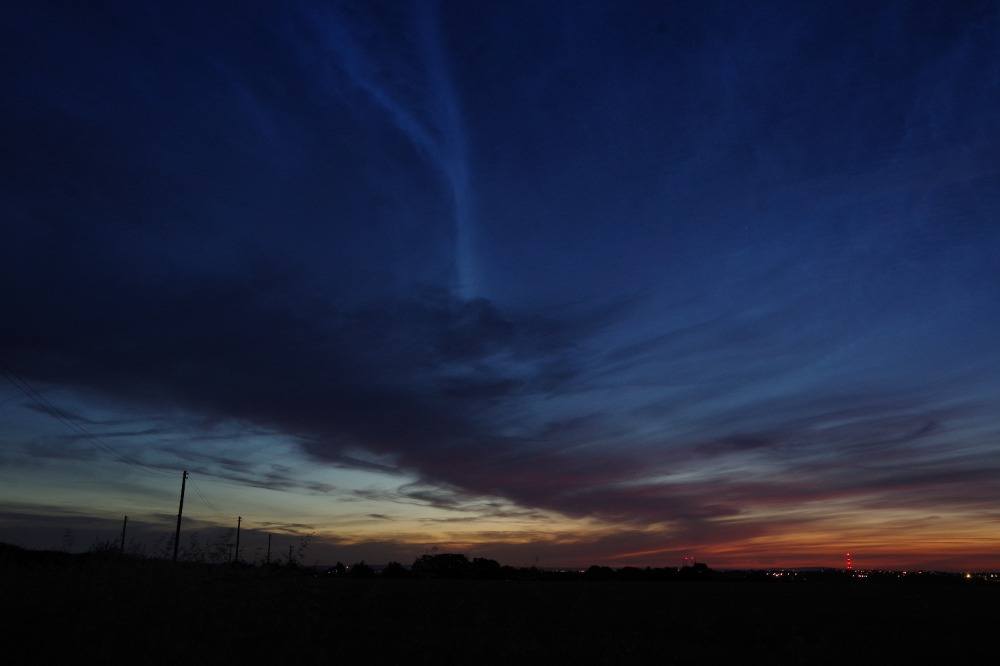
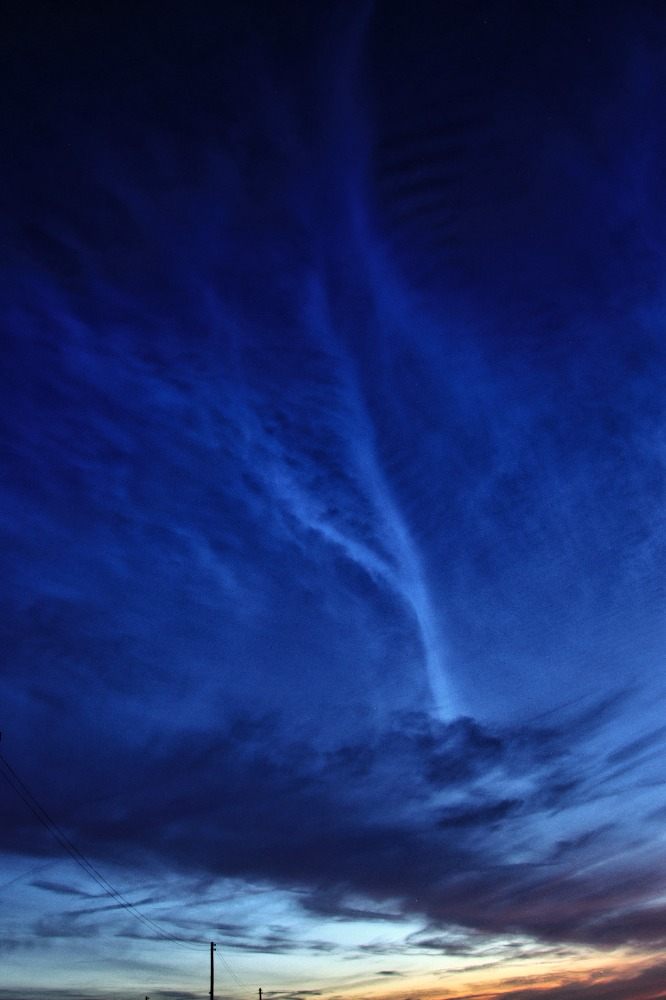
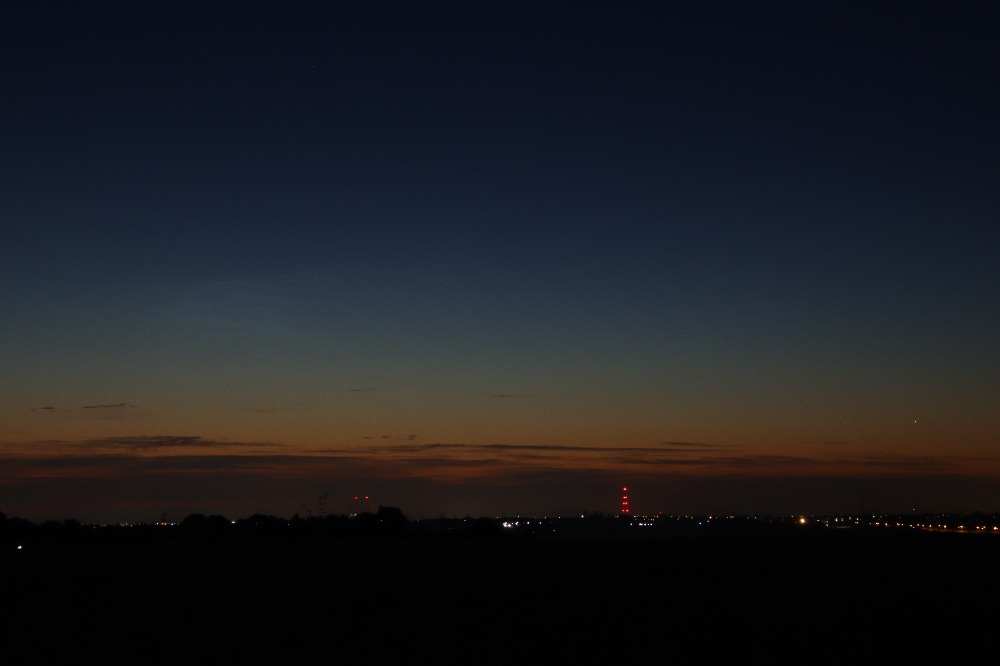
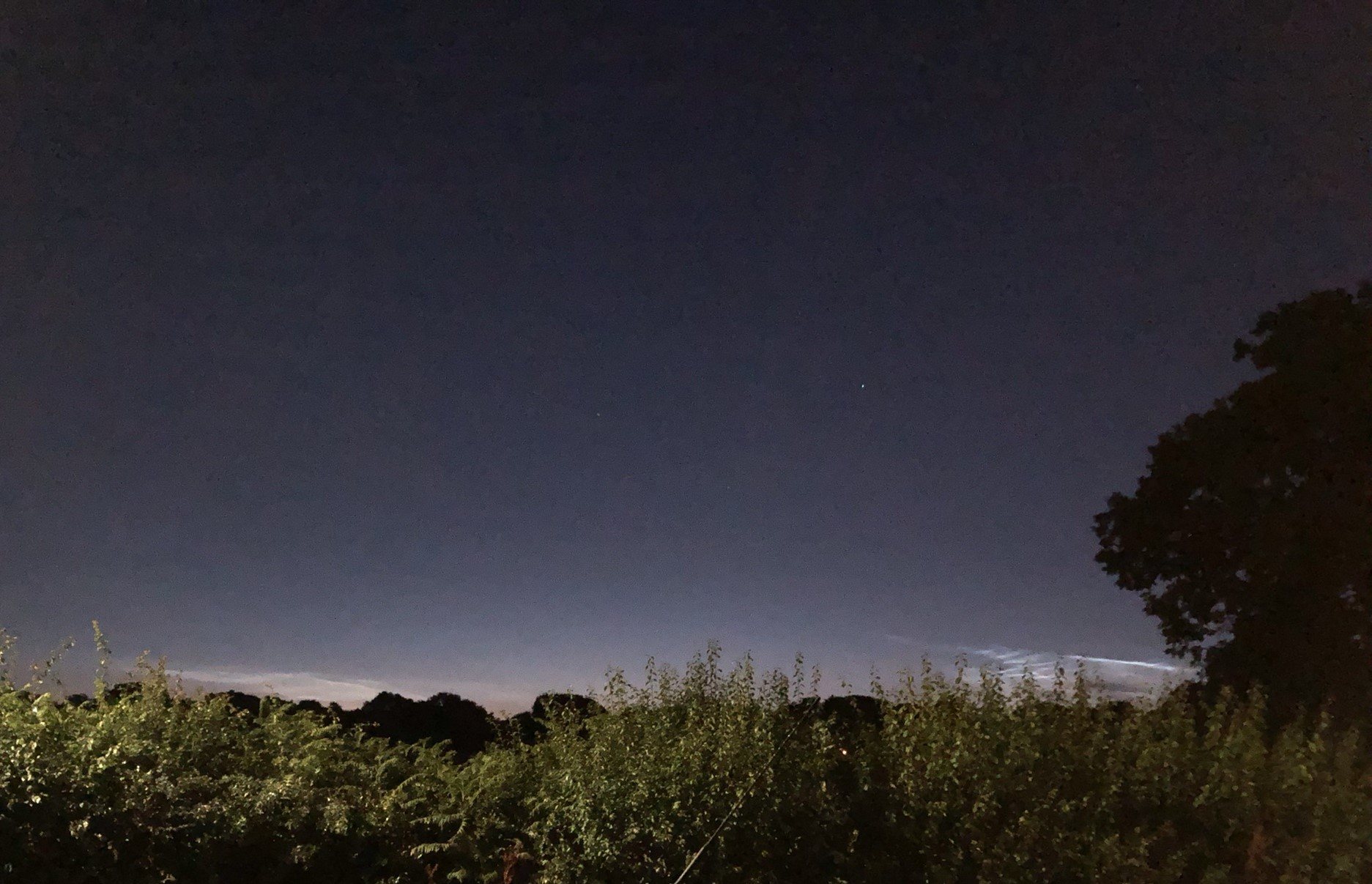
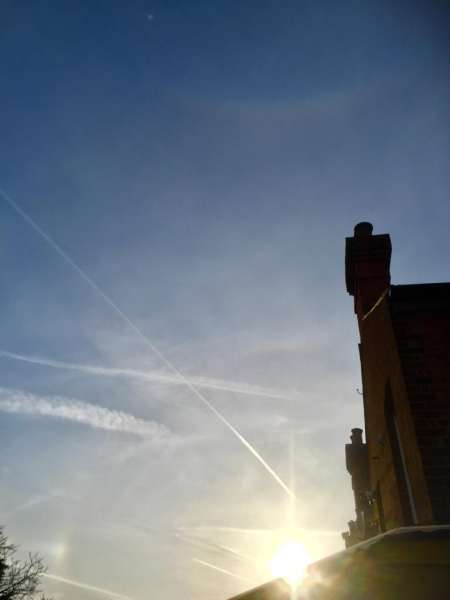
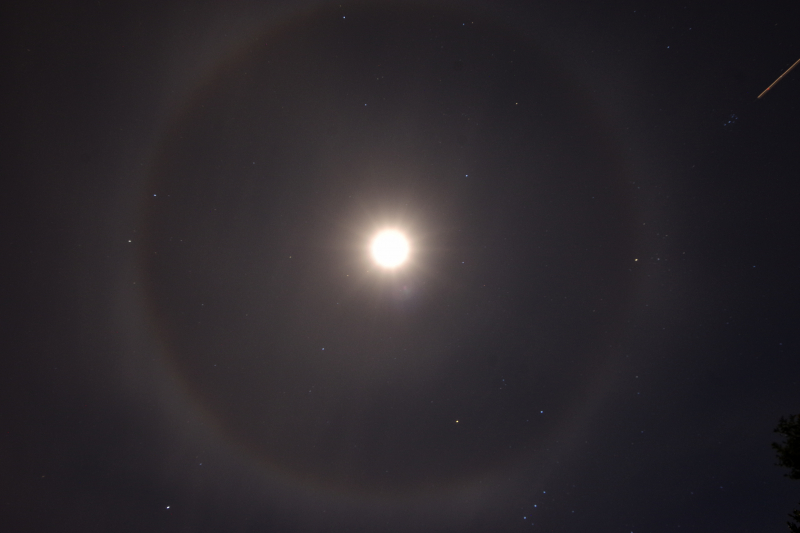
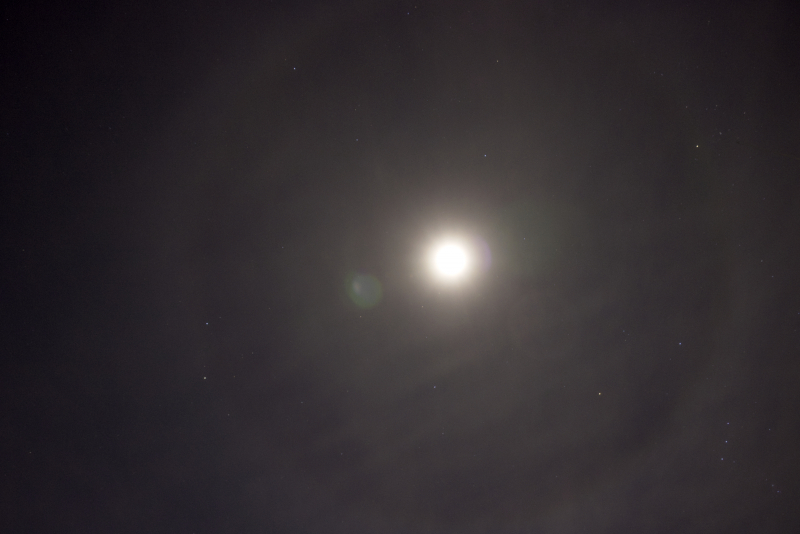
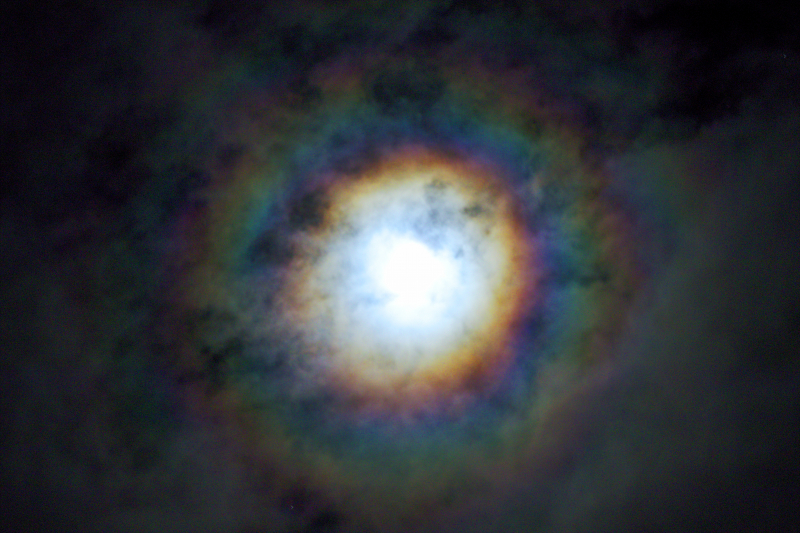
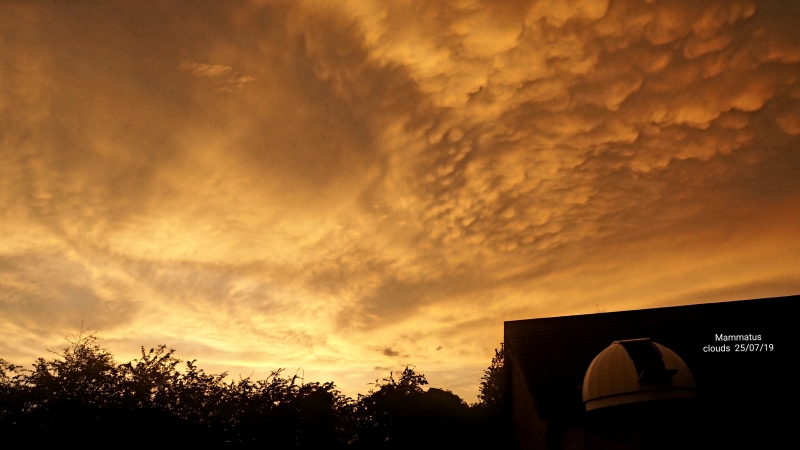
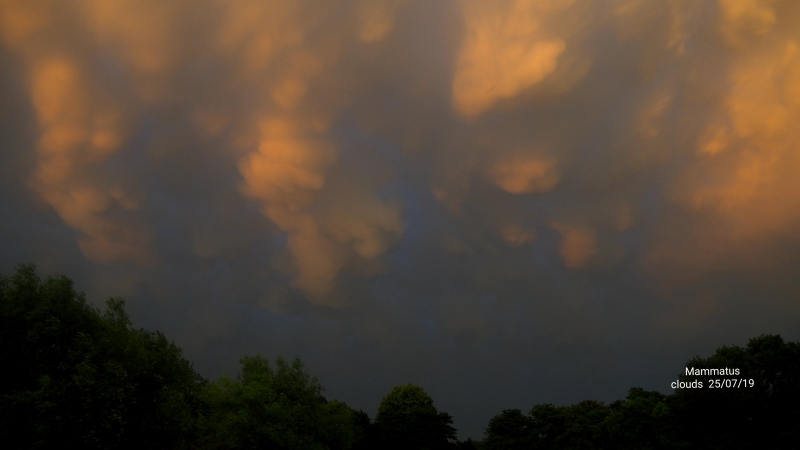
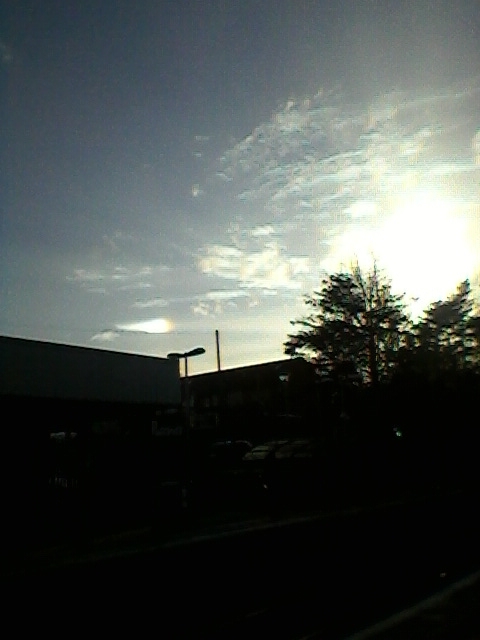
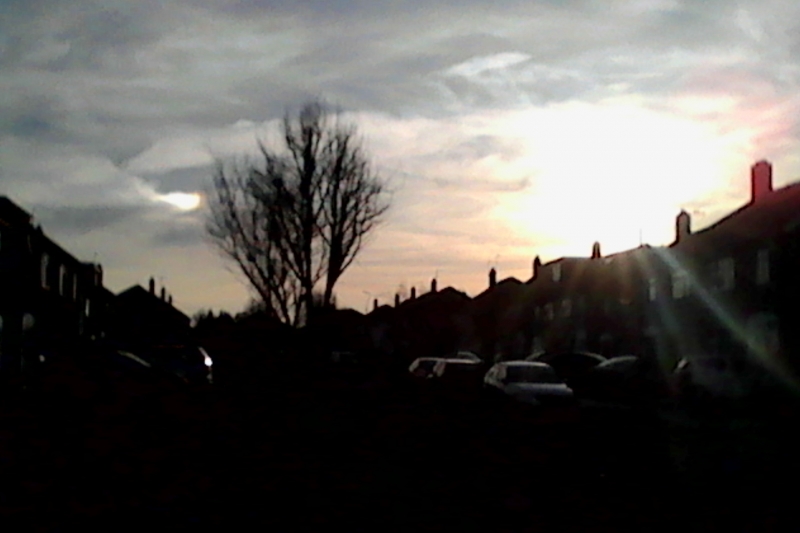
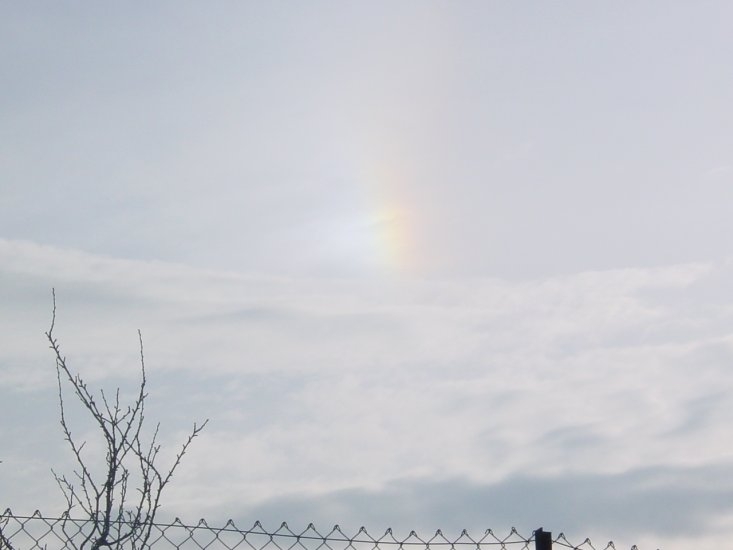
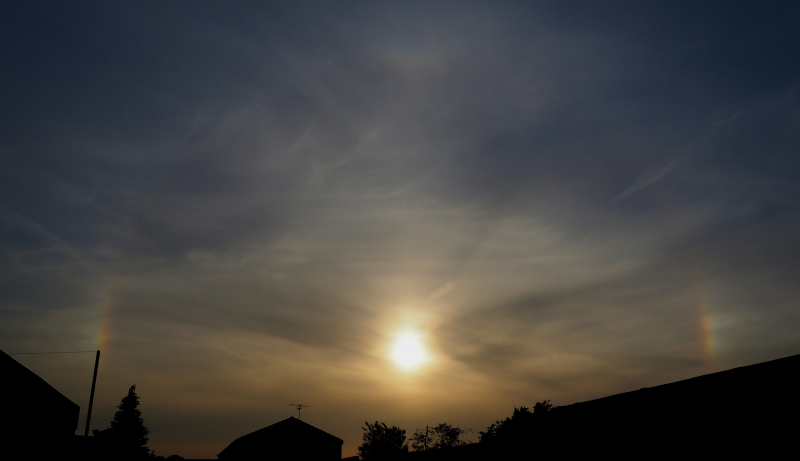
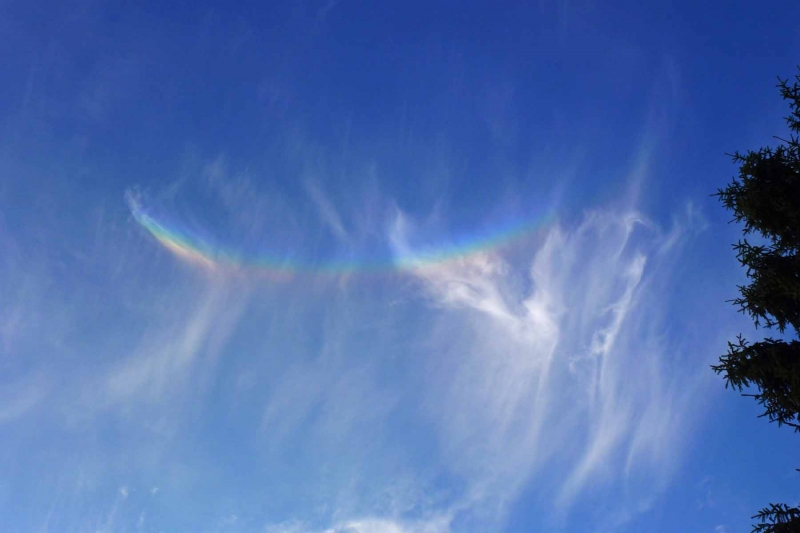
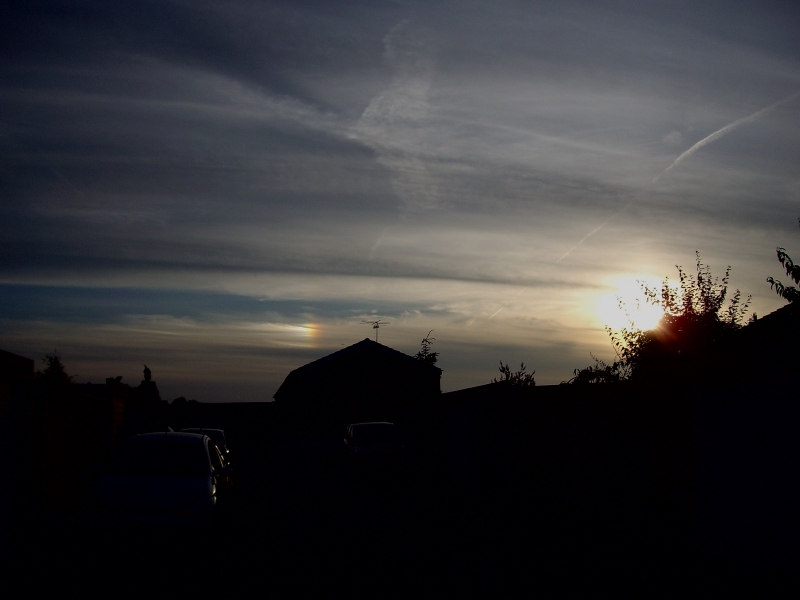
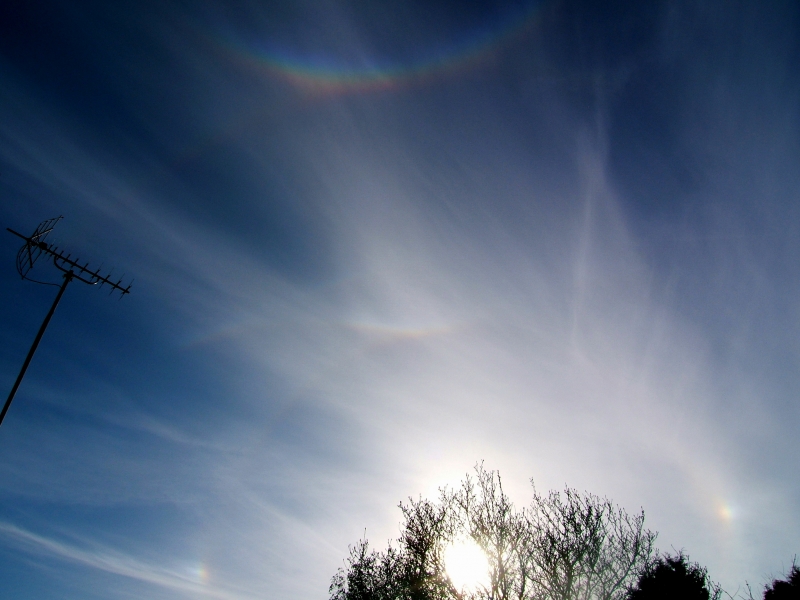
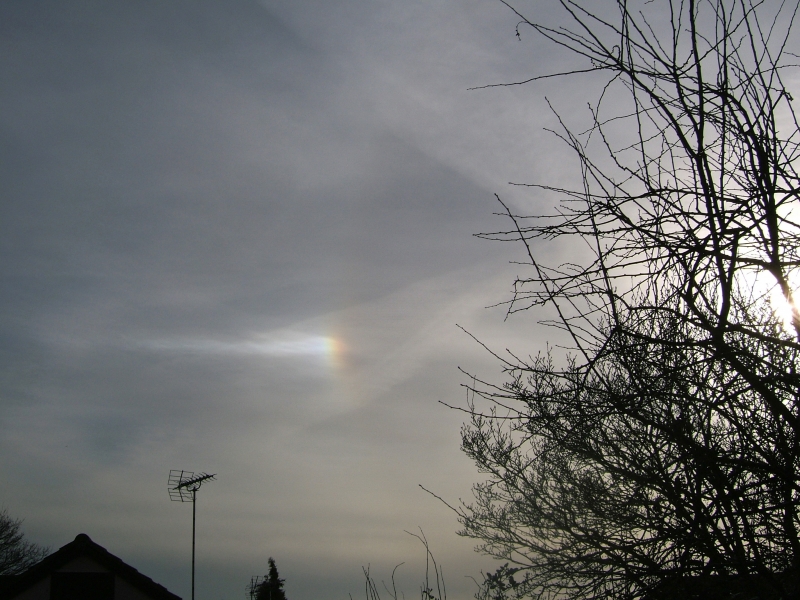
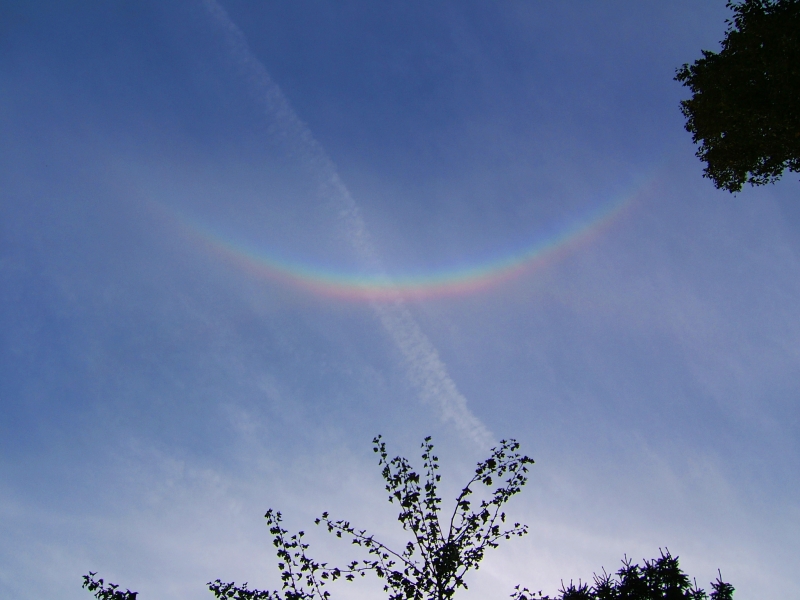
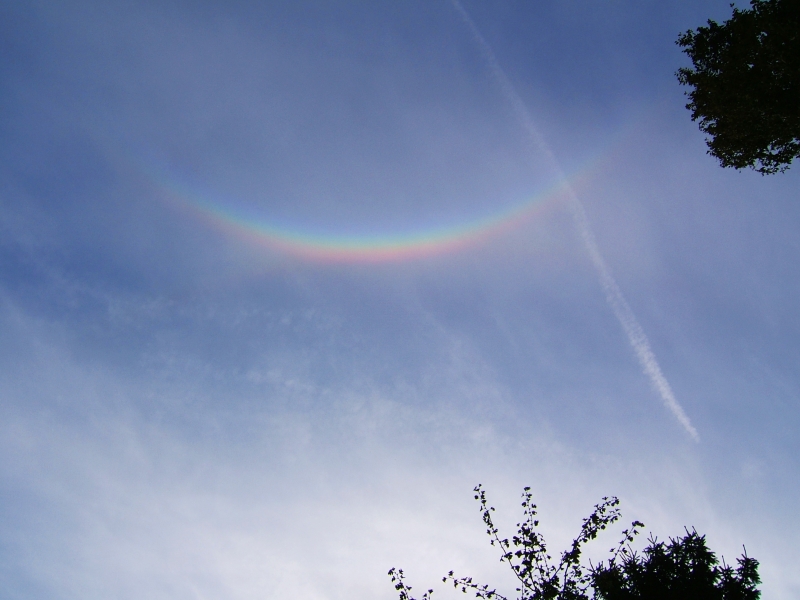
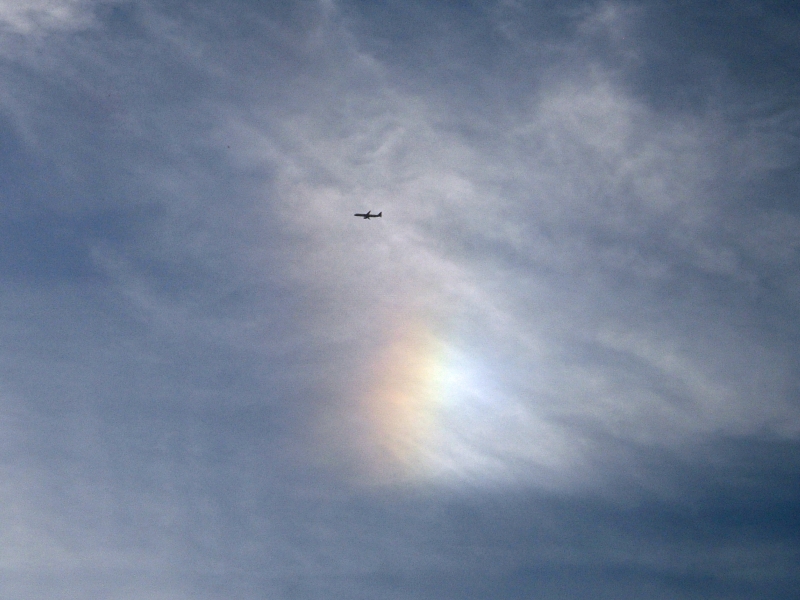
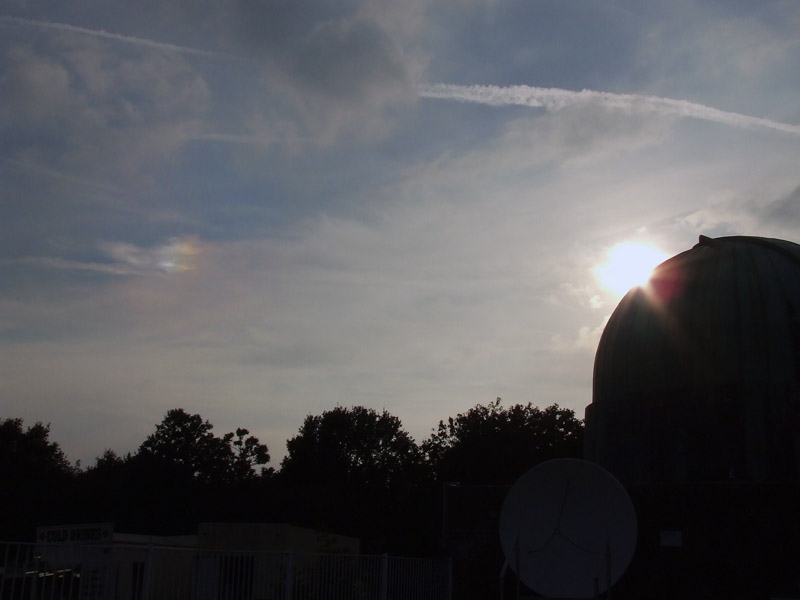
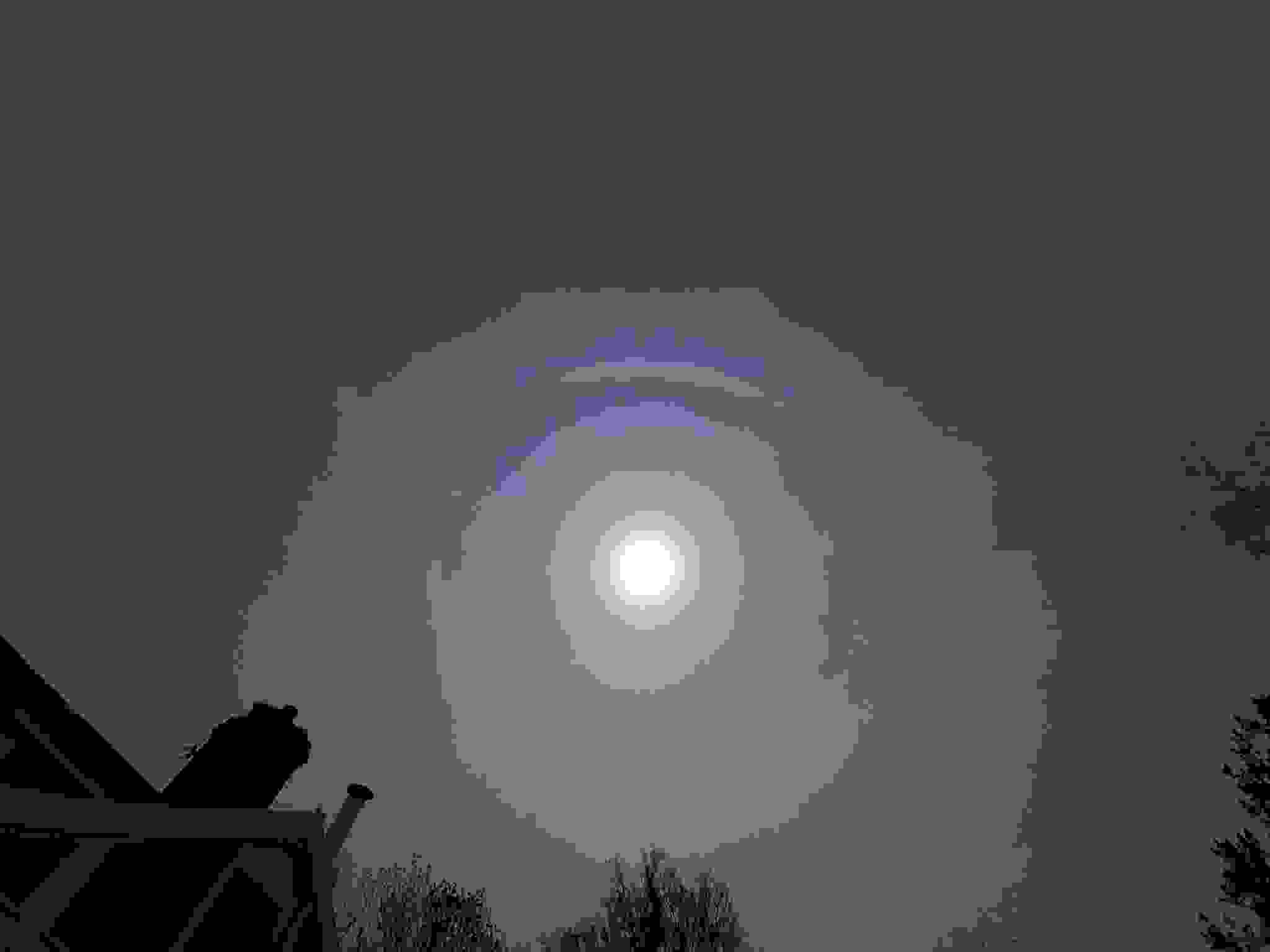
Crepuscular rays at the pavilion by Honor Wheeler
A lovely image taken by member Honor Wheeler on the 10th August 2023 whilst at the pavilion on an informal night of some crepuscular rays.
”Crepuscular rays are sunbeams that originate when the Sun is just above or below a layer of clouds, during the twilight period; which extend over the western sky radiating from the position of the Sun. Crepuscular comes from the Latin word crepusculum meaning “twilight”. Loosely, the term crepuscular rays is sometimes extended to the general phenomenon of rays of sunlight that appear to converge at a point in the sky, irrespective of time of day.” Ref: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crepuscular_rays
”The radiating appearance of the bands is caused by perspective, as demonstrated by the fact that when on rare occasions the rays extend across the entire sky, they appear to converge again on the eastern horizon. This rare related phenomena are called anticrepuscular rays and so appear at the same time (and coloration) as crepuscular rays but in the opposite direction of the setting sun (east rather than west).” Ref: https://www.britannica.com/science/crepuscular-ray

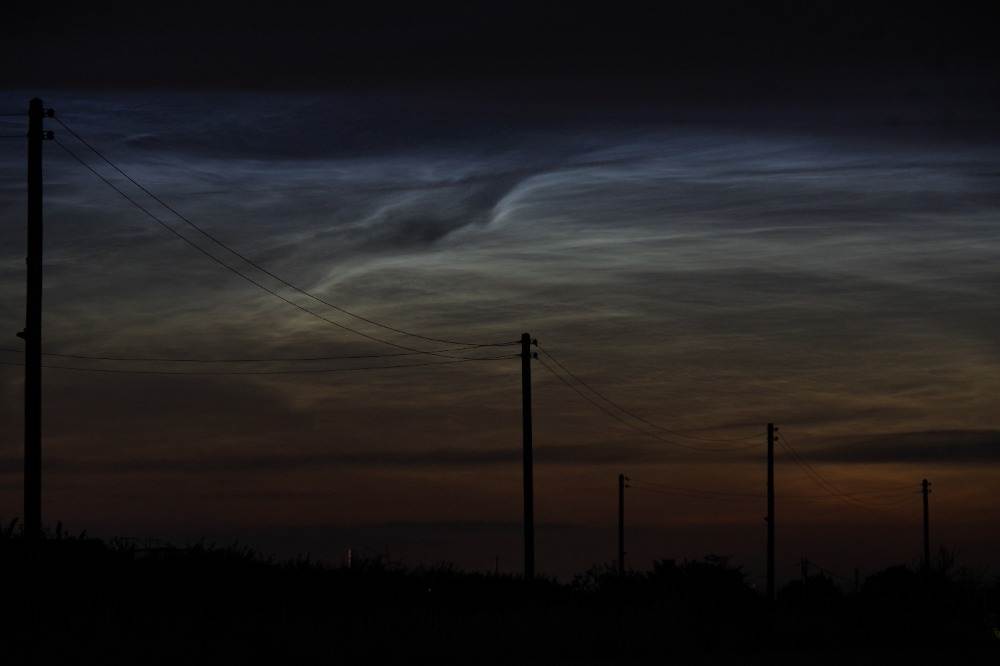
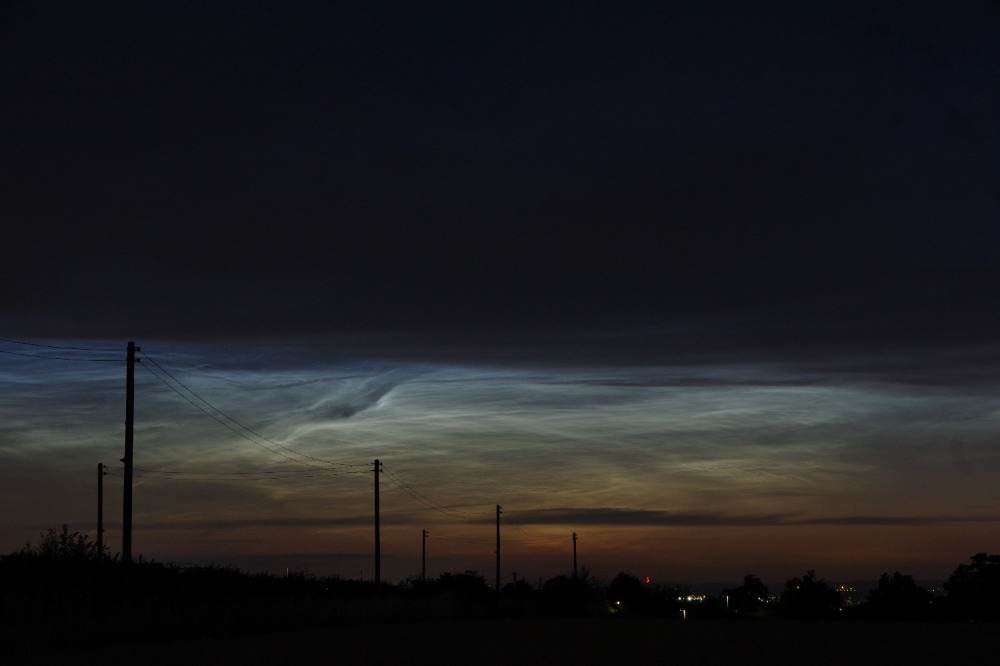
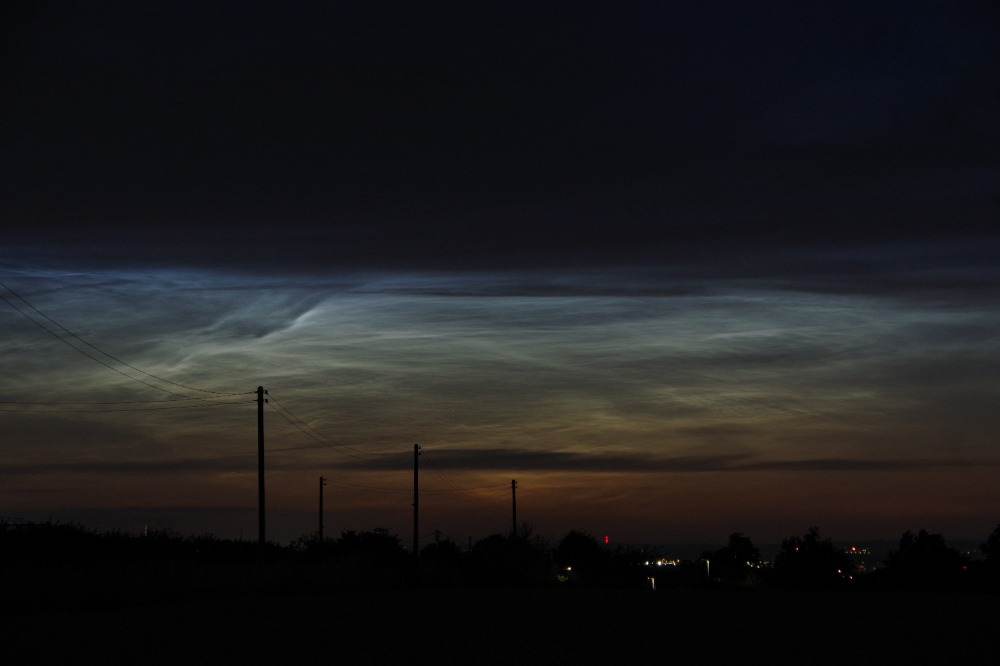
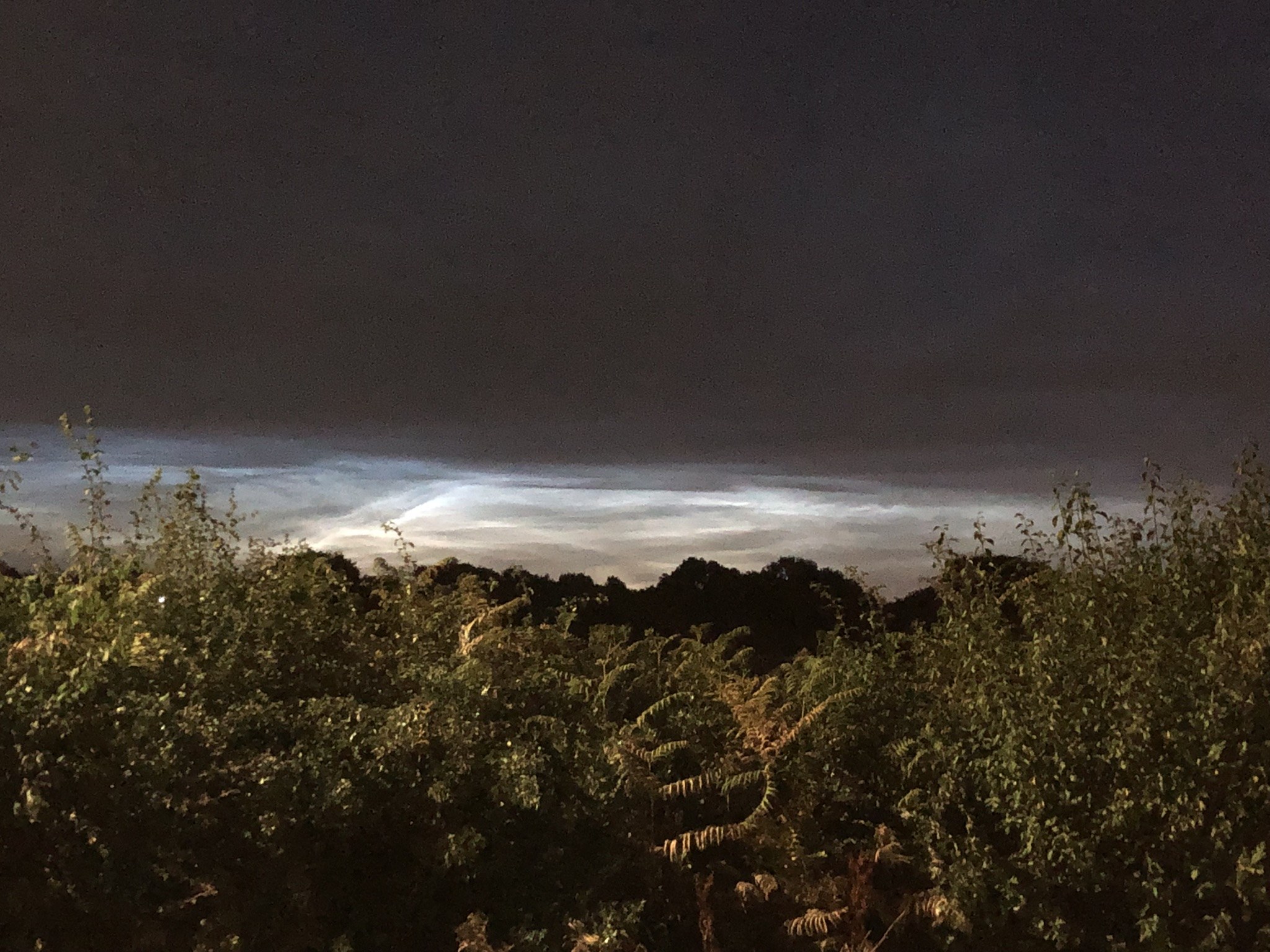
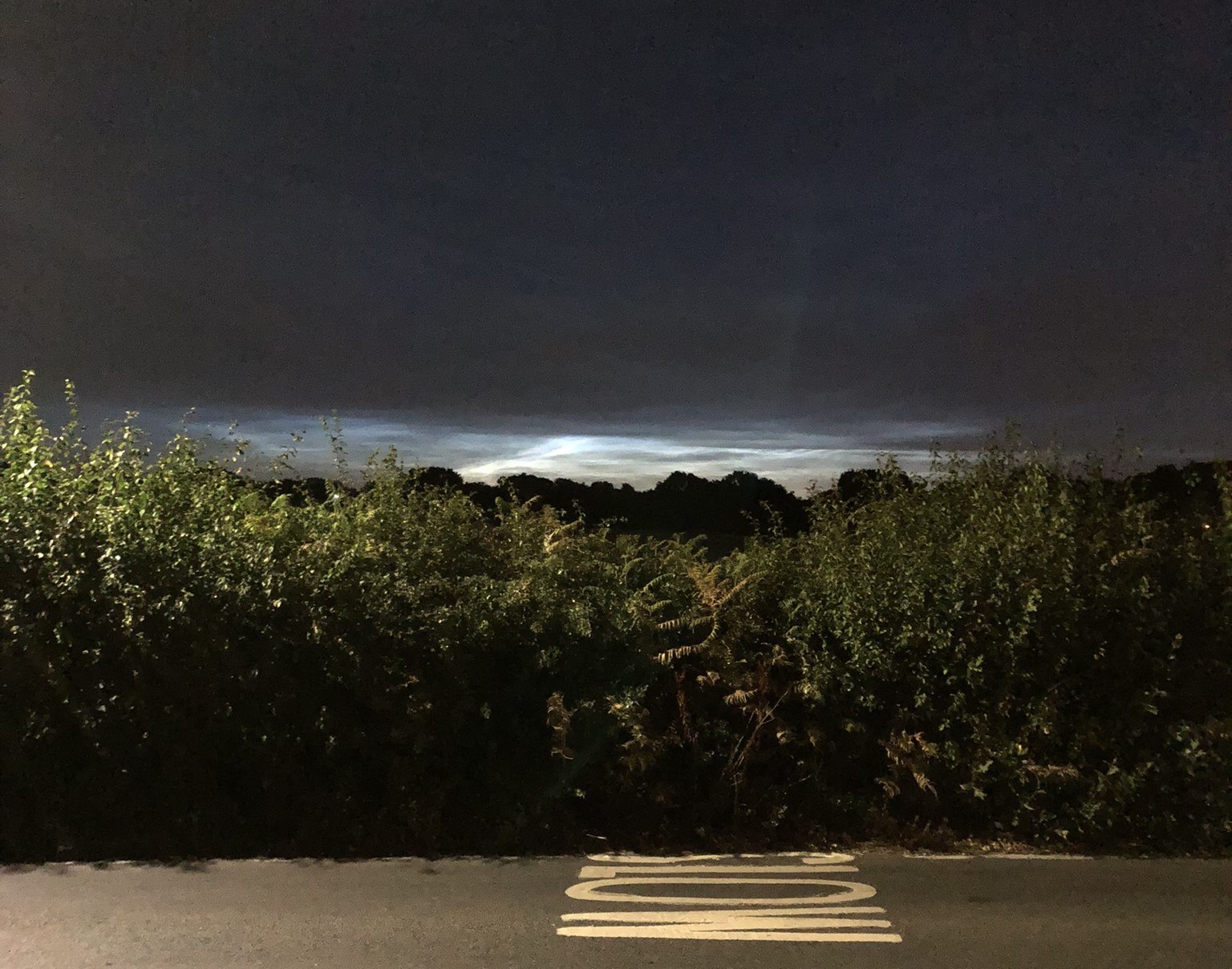
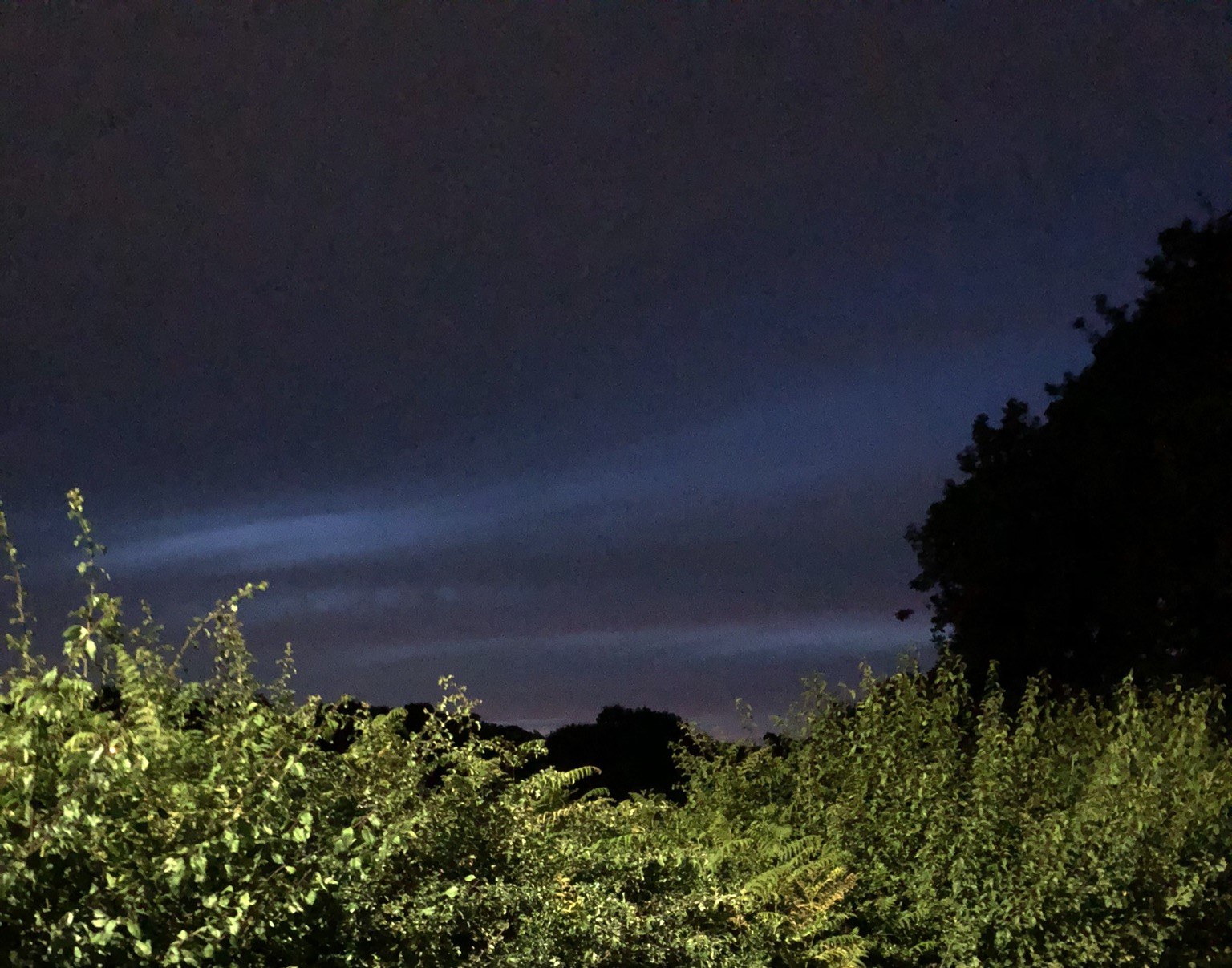
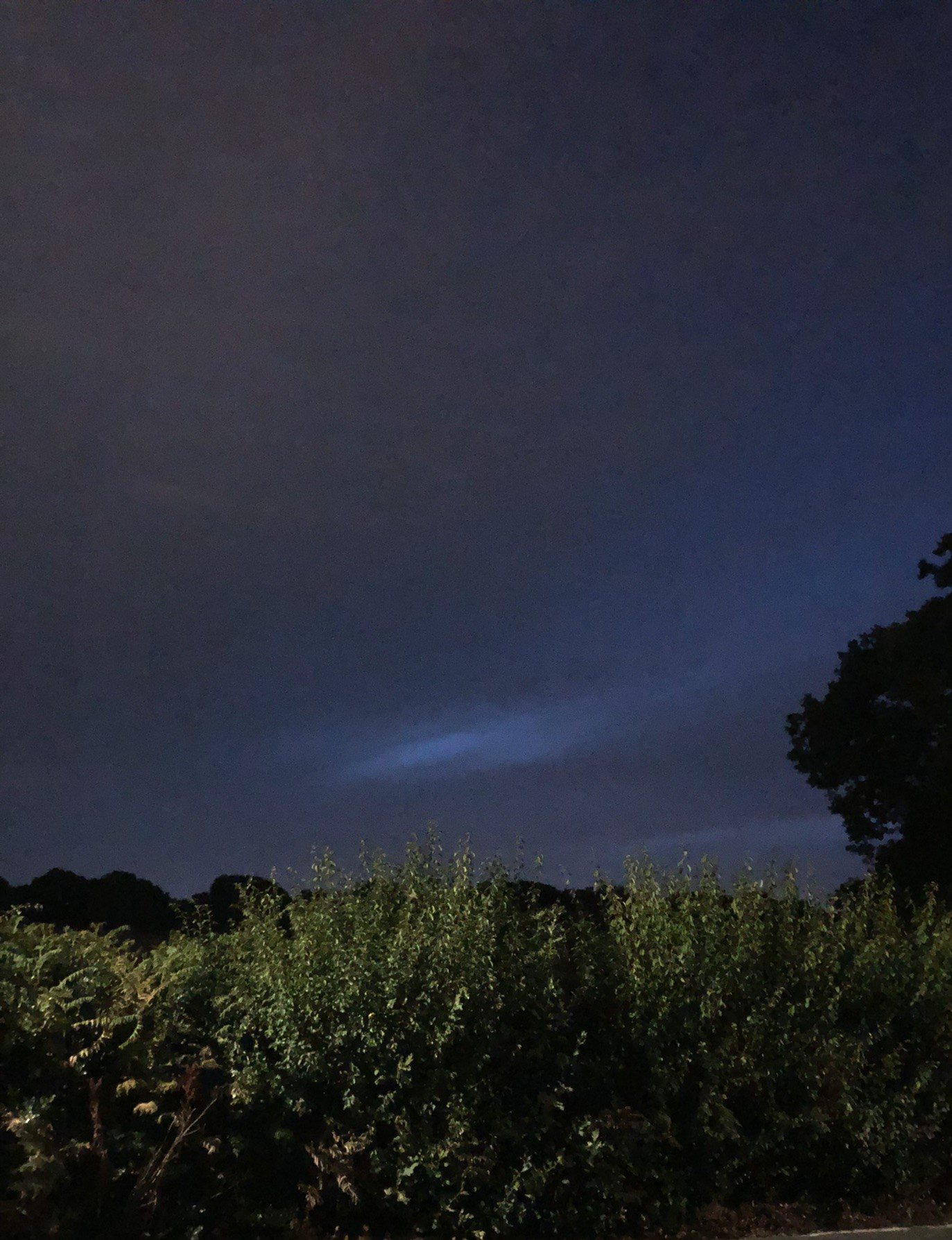
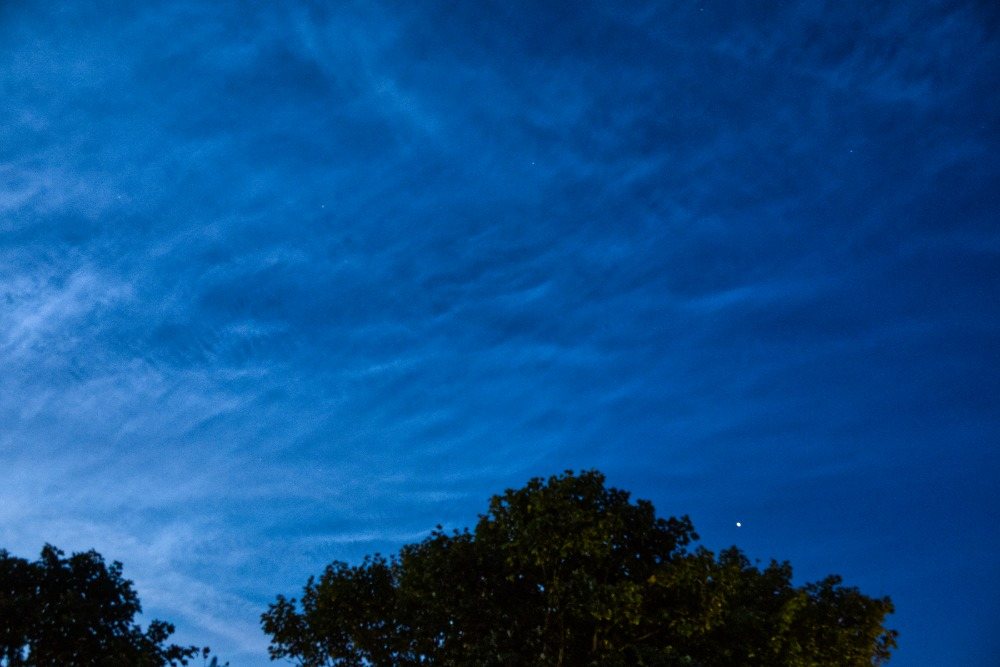
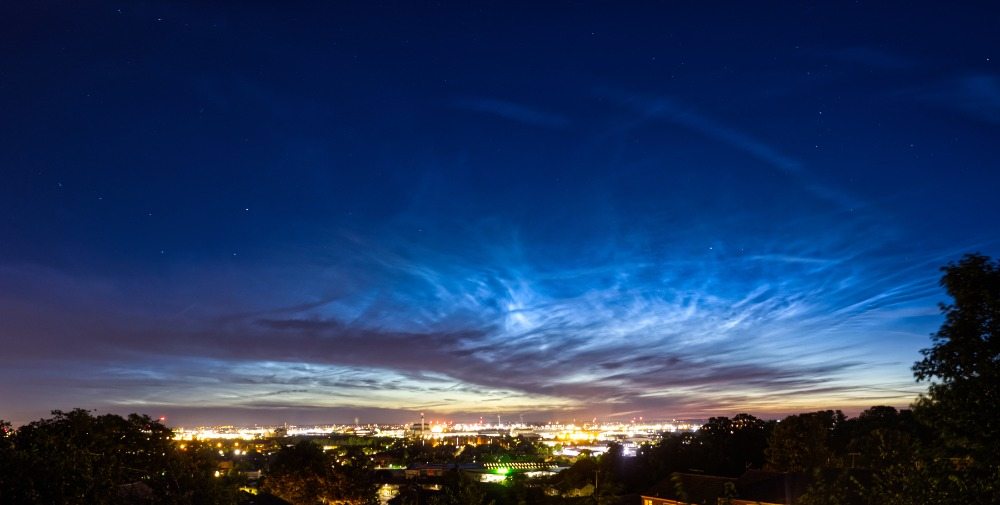
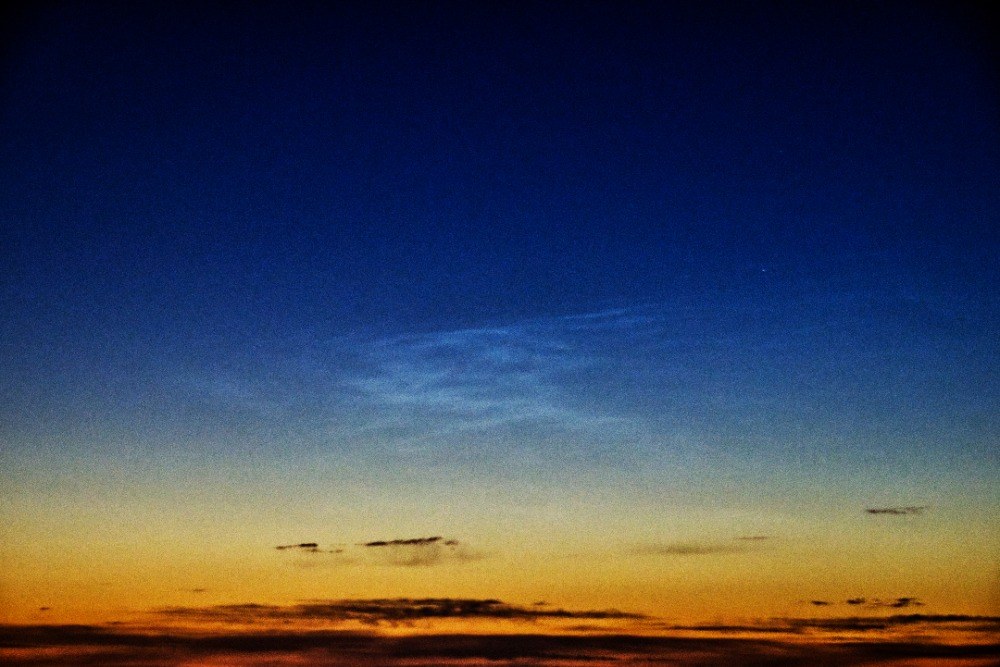
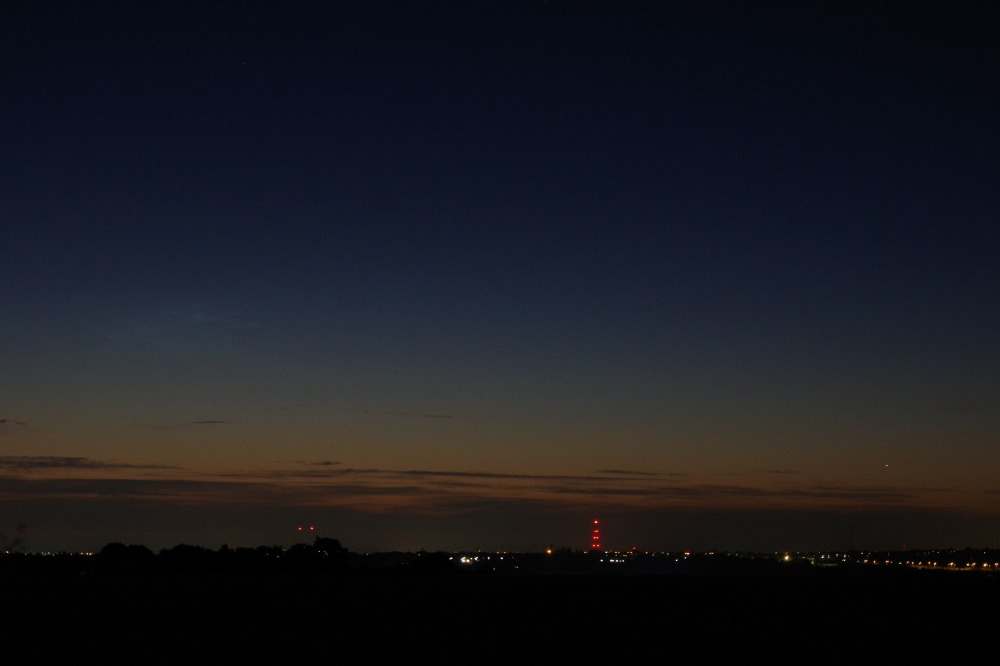
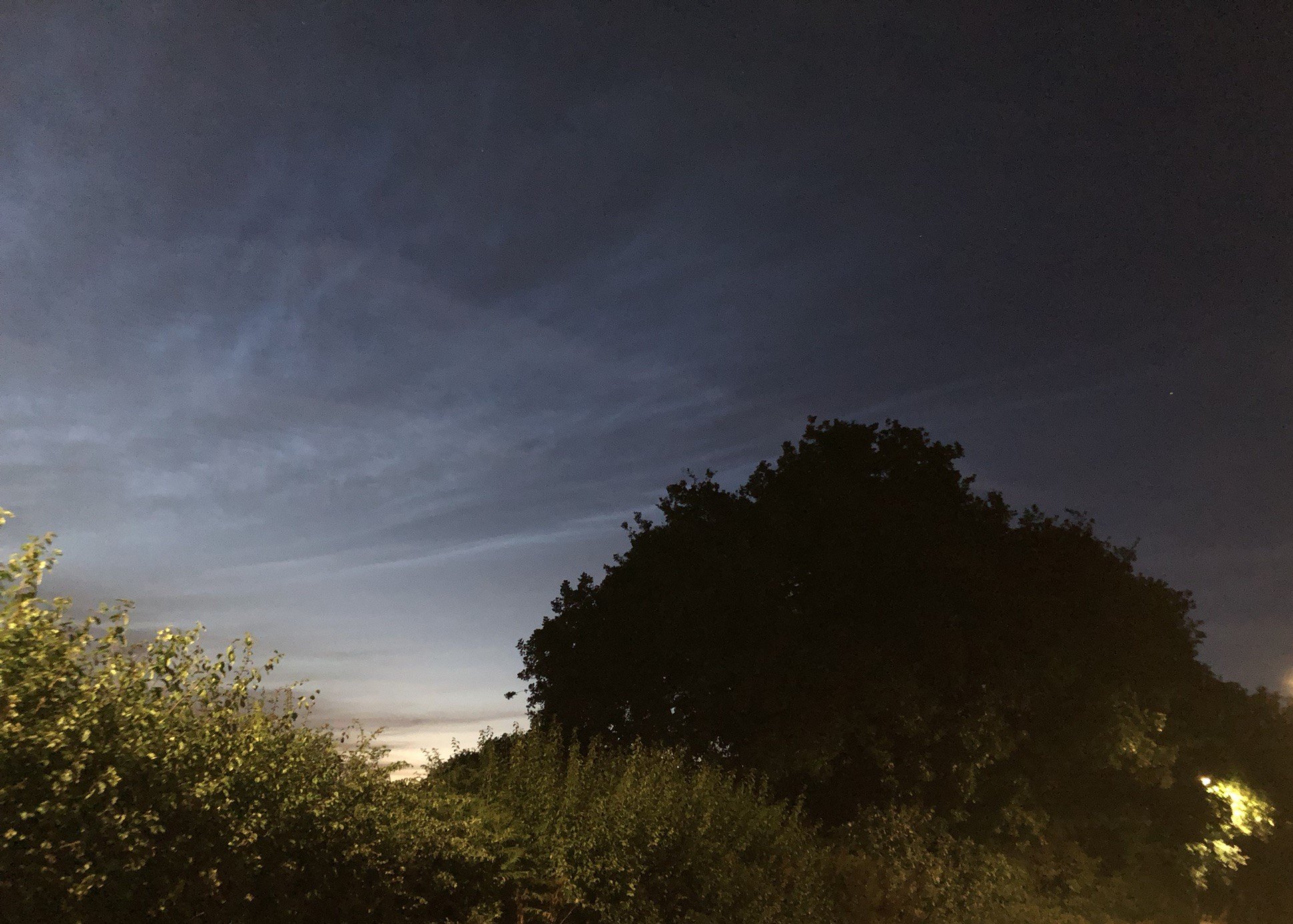
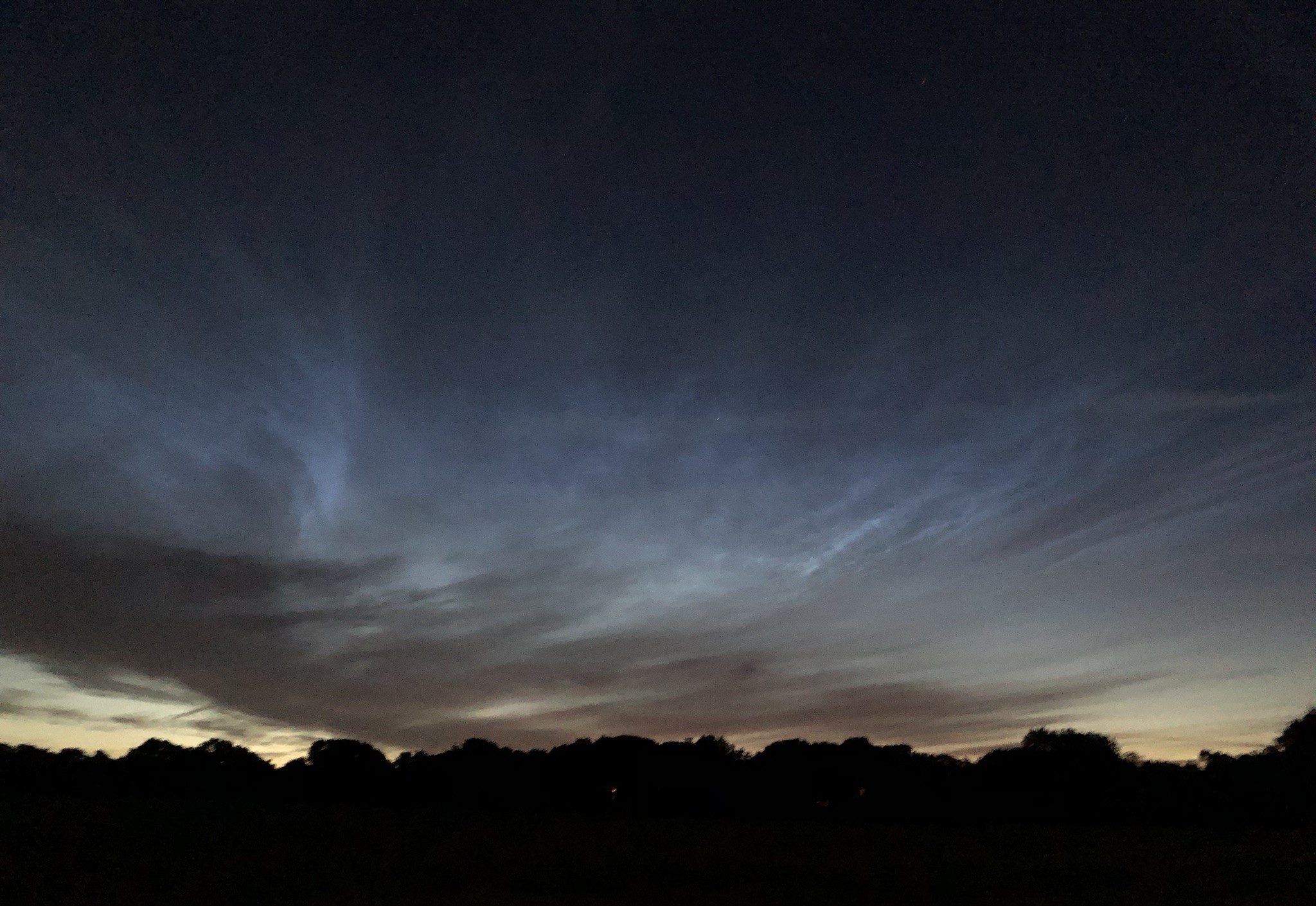
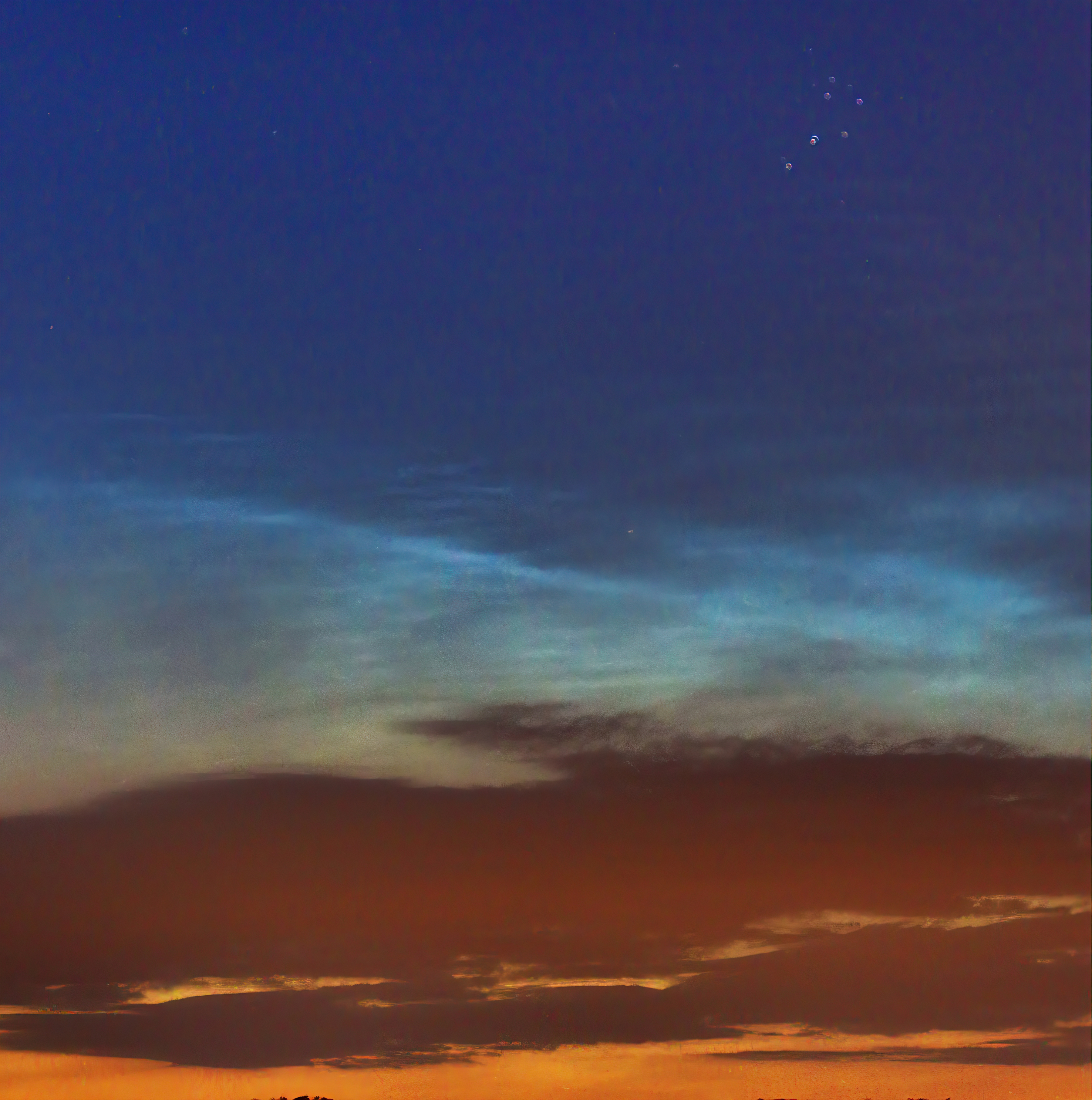
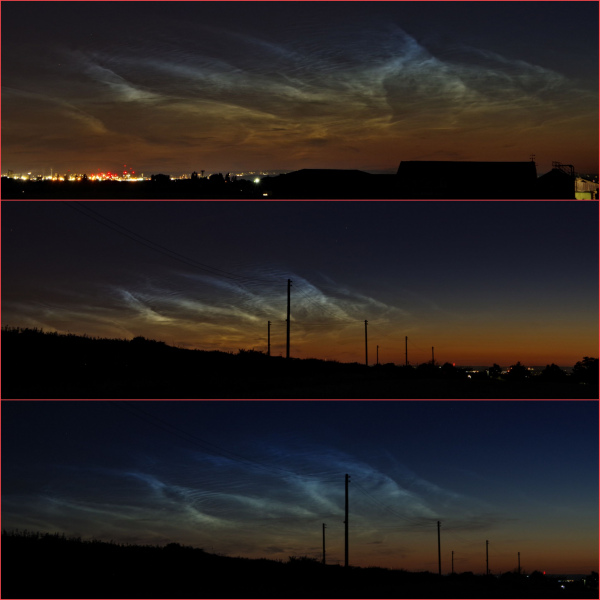
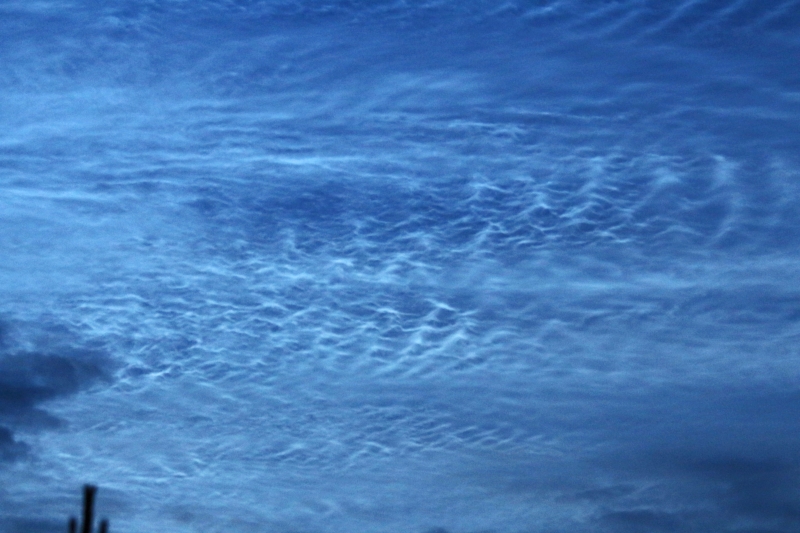
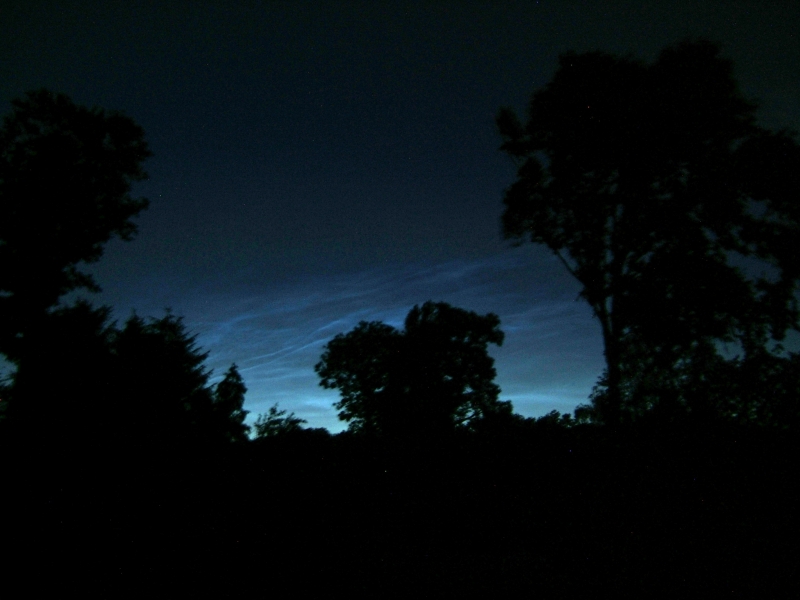
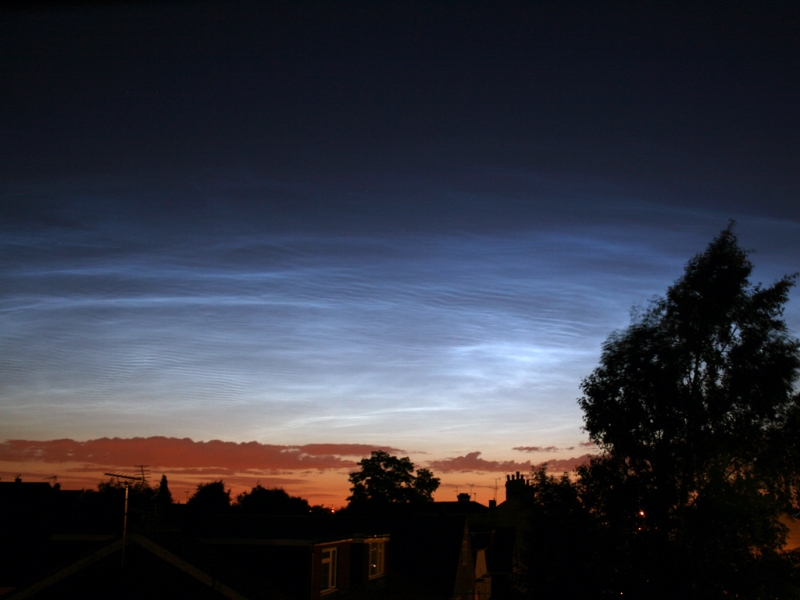
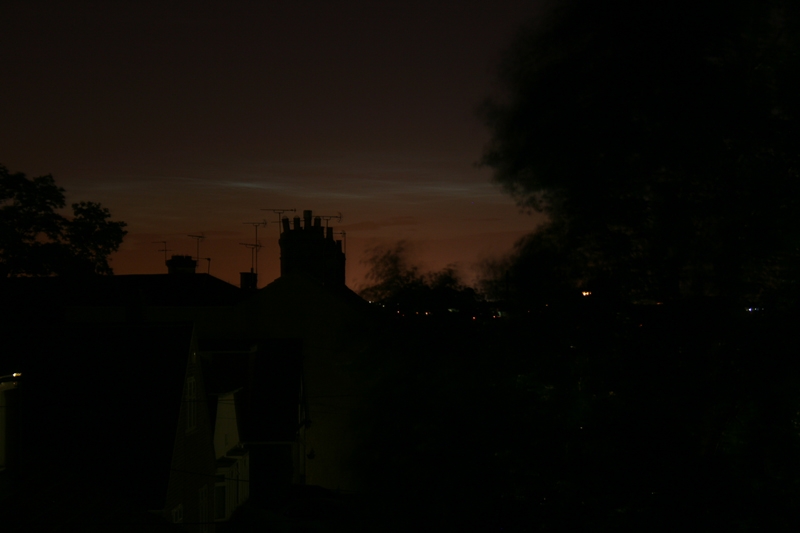
Noctilucent Cloud (NLC) – 5th July 2023
Noctilucent clouds put in a rare appearance on the 5th July 2023 from around 10.50pmish until 11.30pm and a few lucky CMHASD members got to see them 🙂
Below are the photos that members Jim Burchell, Diane Clarke, Martin Crow and Sonia took of the clouds.
Jim’s NLC images, taken with a Pentax KP.


Diane’s NLC image, taken using a Canon M50 Mk2, lens Canon 100mm macro, f3.2 @ 2.5sec, ISO 400.

Martin’s NLC image, taken with an iPhone.

Sonia’s NLC images, taken with an iPhone.


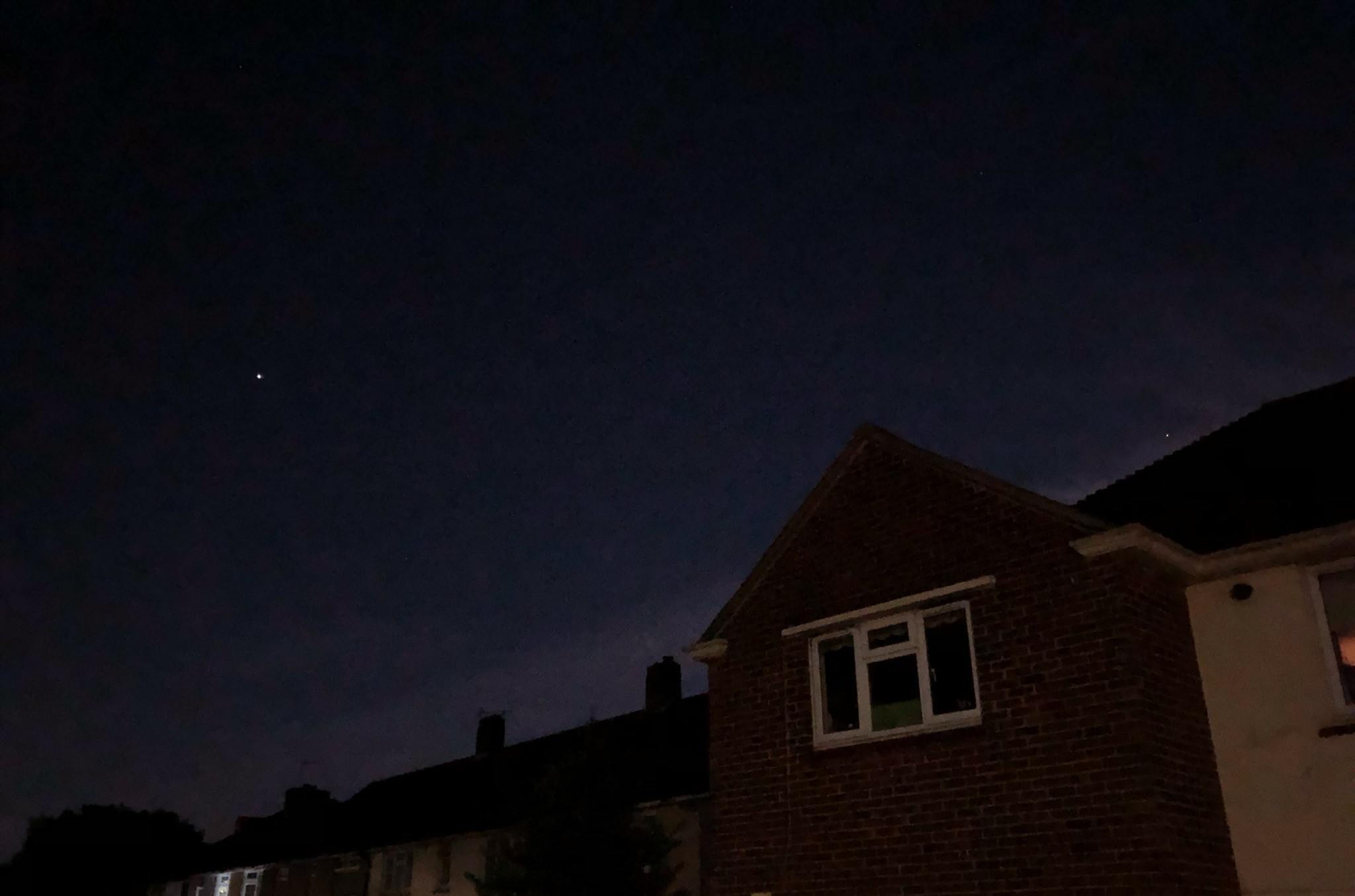
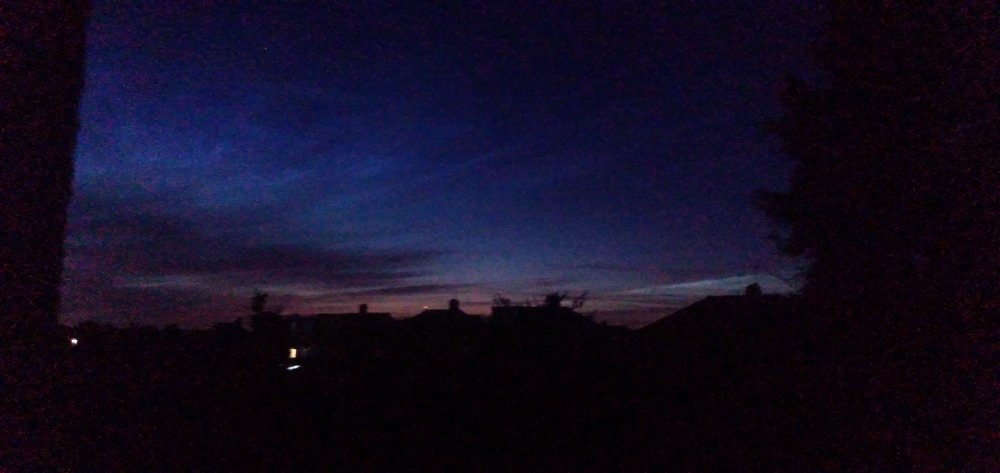
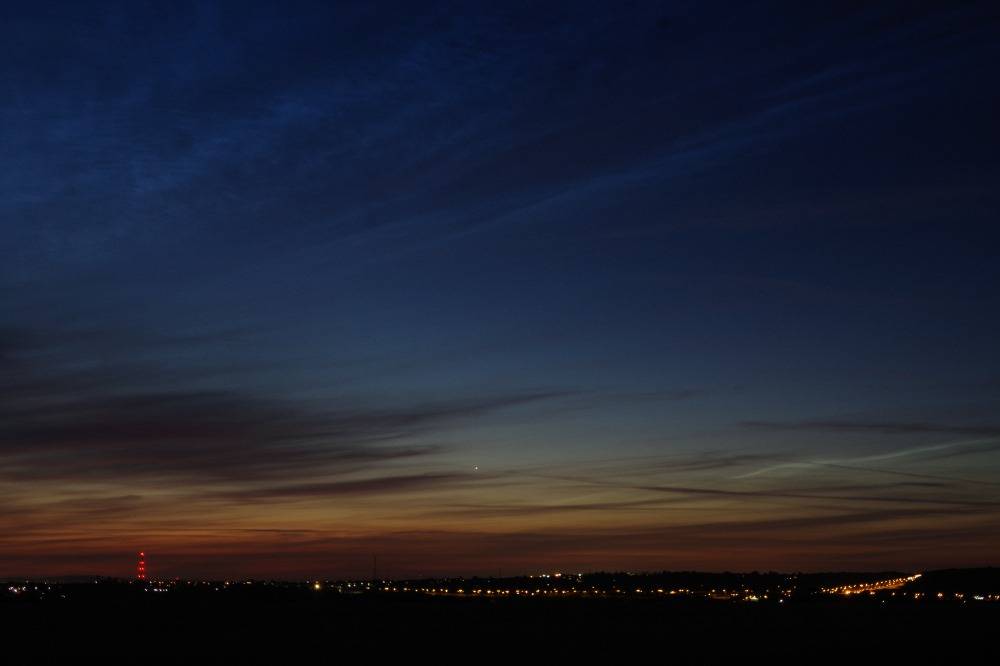
Noctilucent Cloud – 30th June 2023
Noctilucent cloud spotted on the 30th June 2023 around 3am BST by members Martin Crow and Sonia. Both photos taken using an iPhone.
Martin’s image taken from Essex

Sonia’s image taken from North Kent

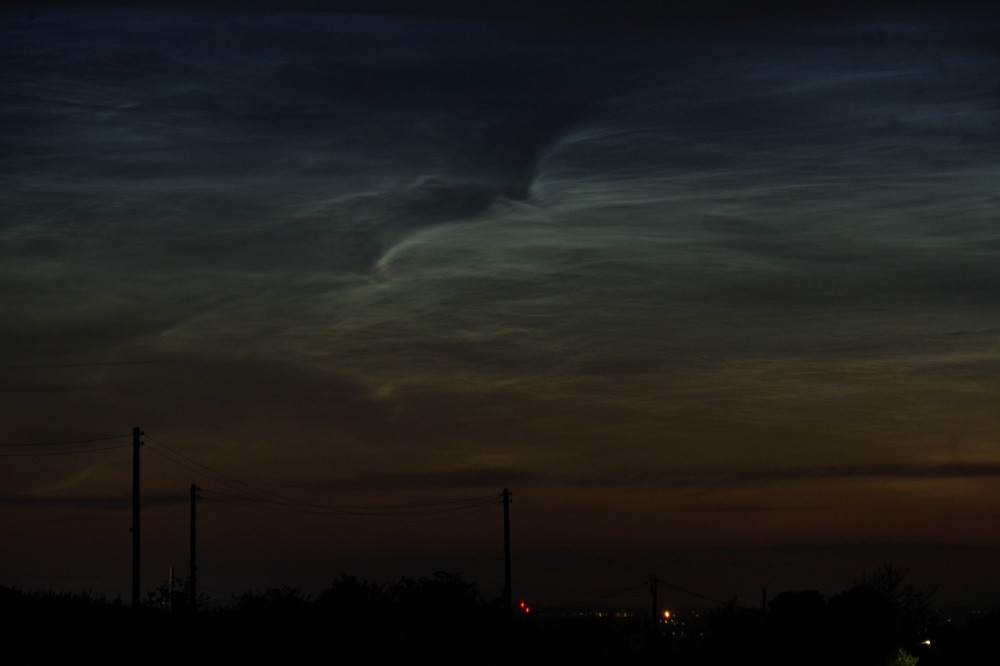
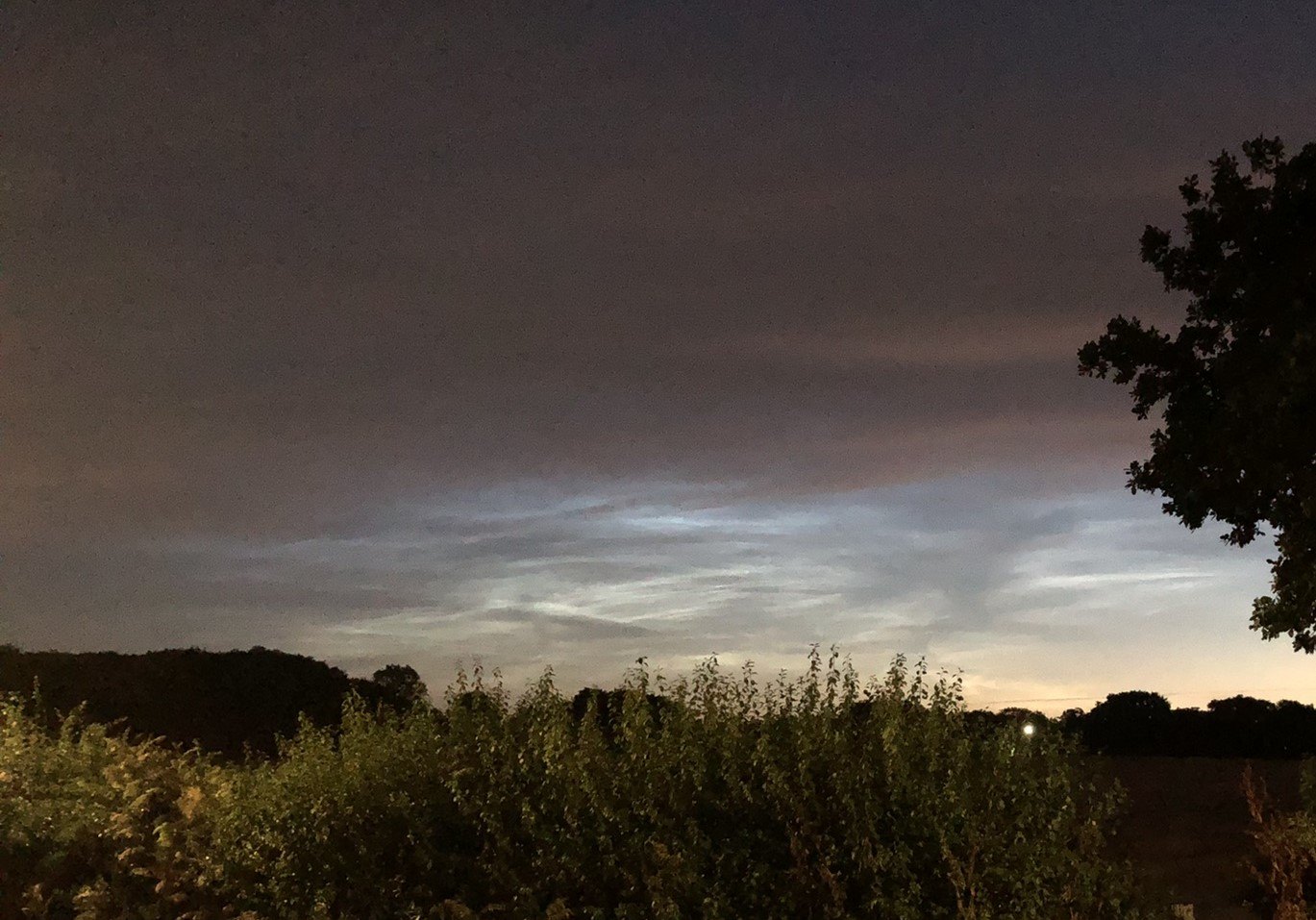
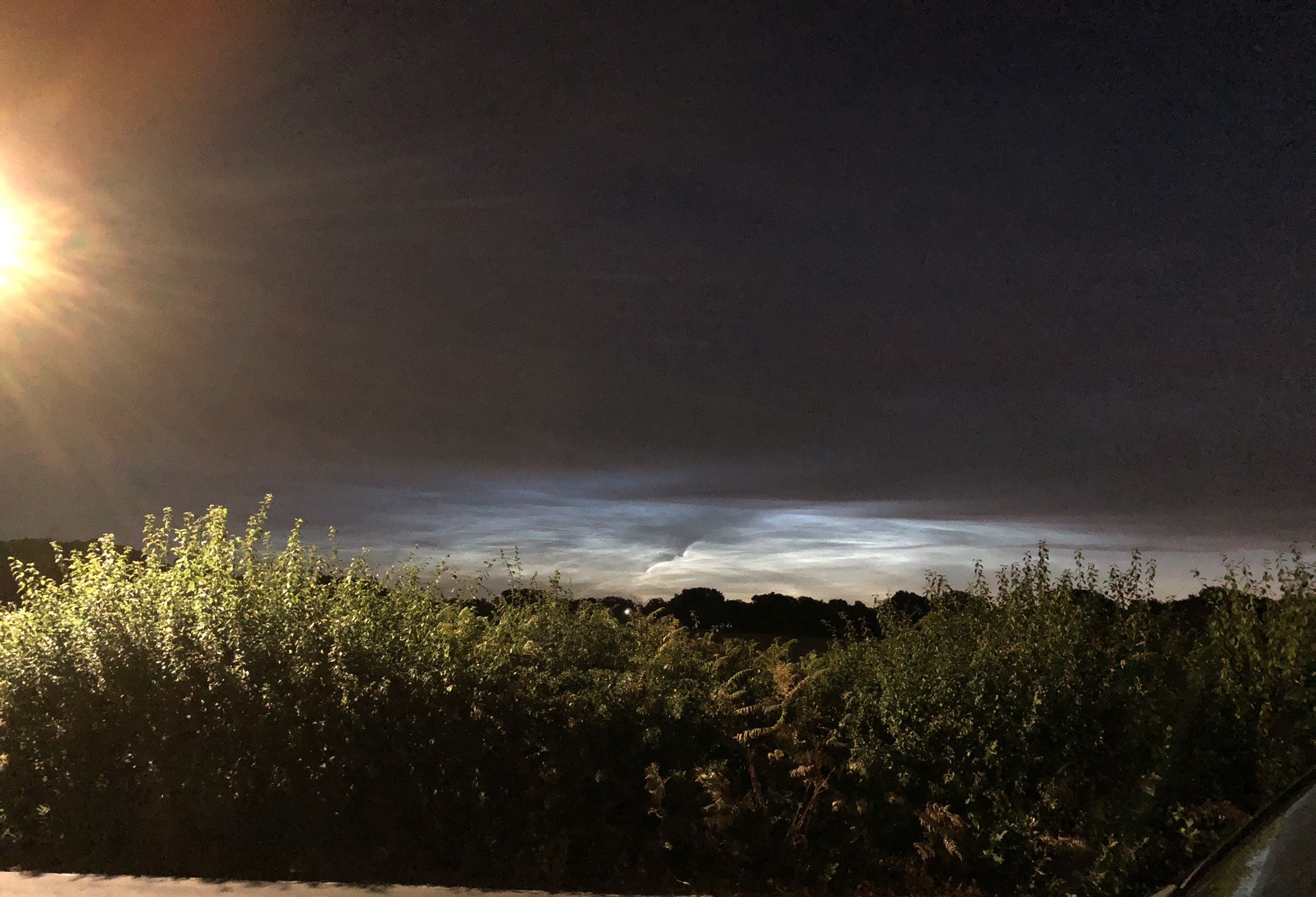
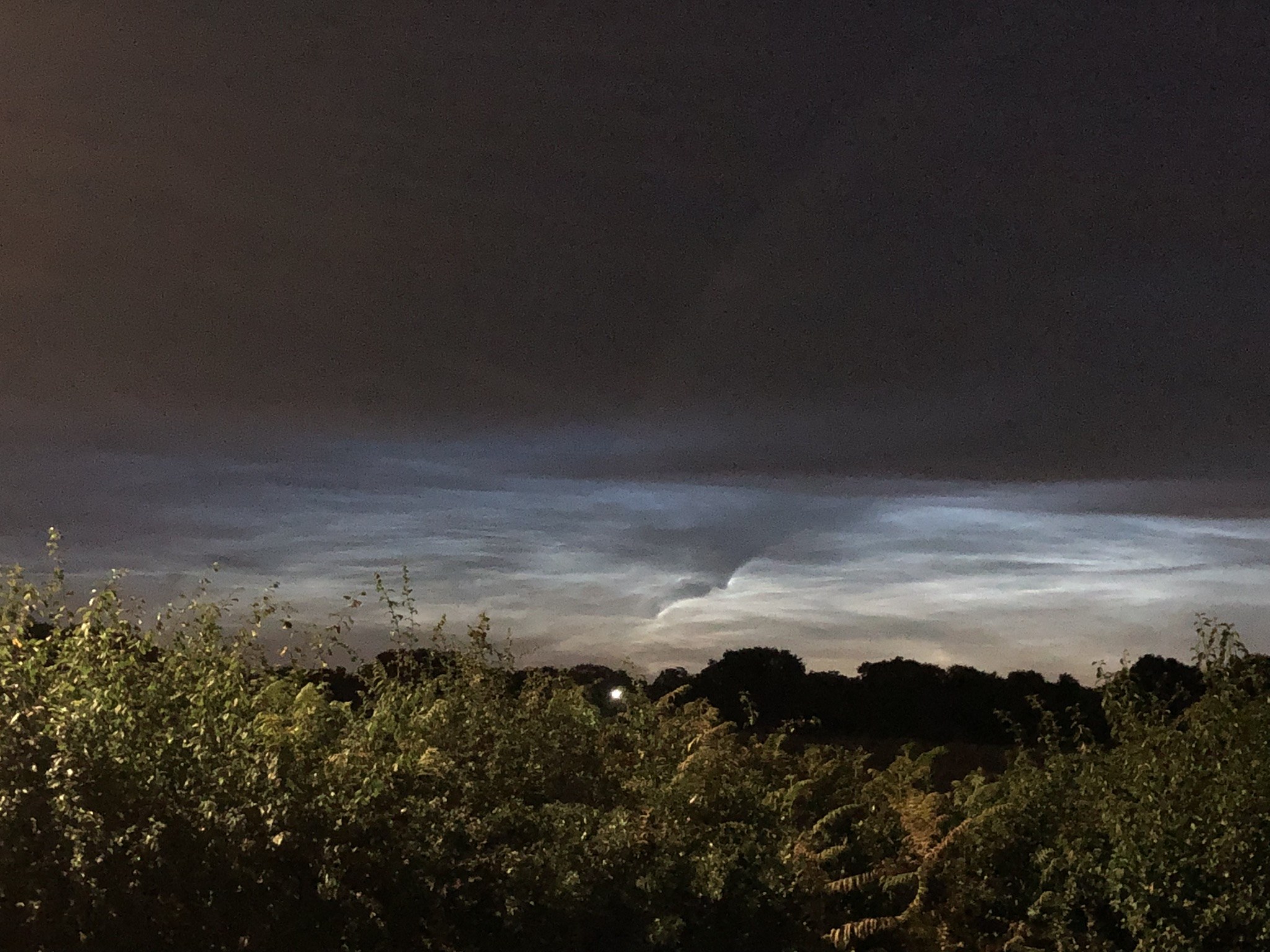
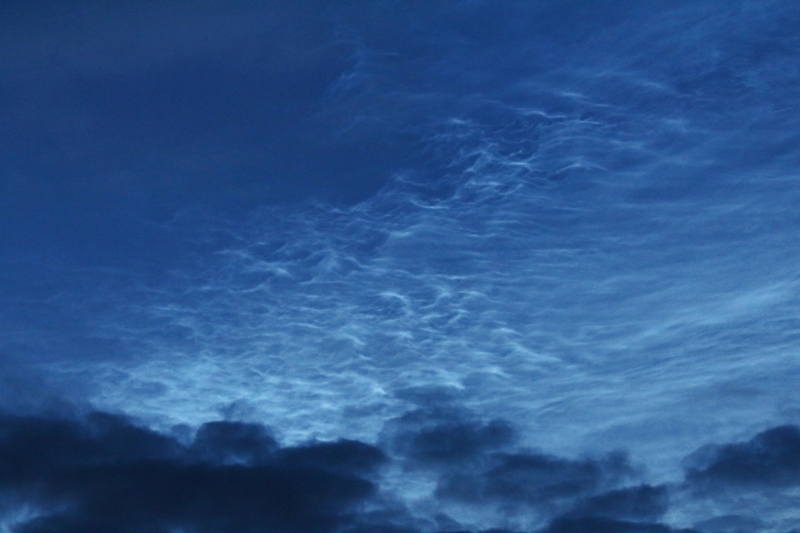
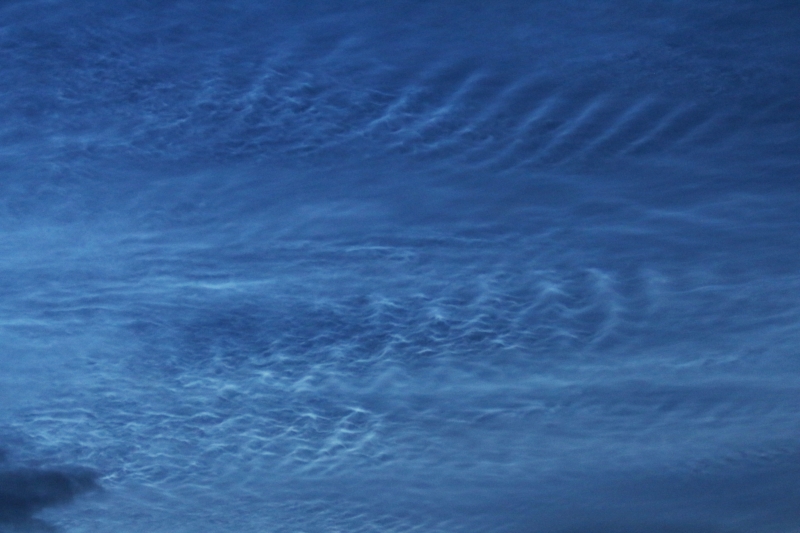
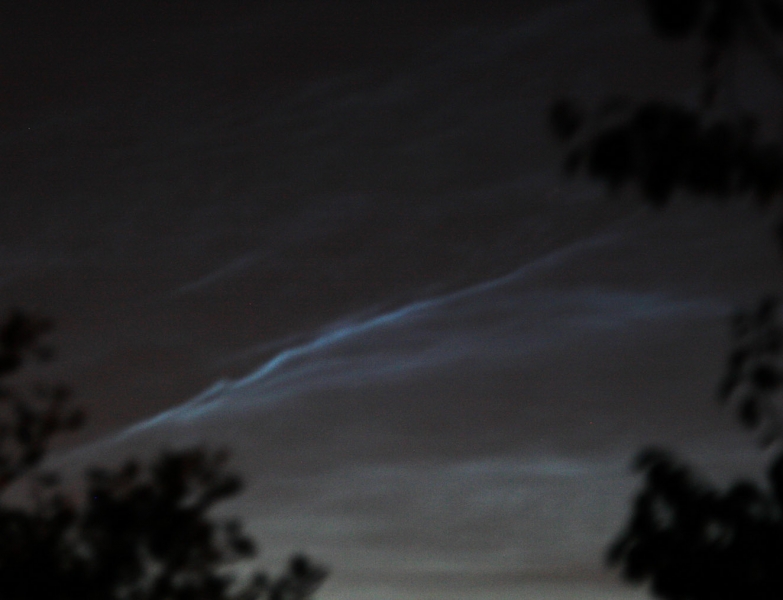
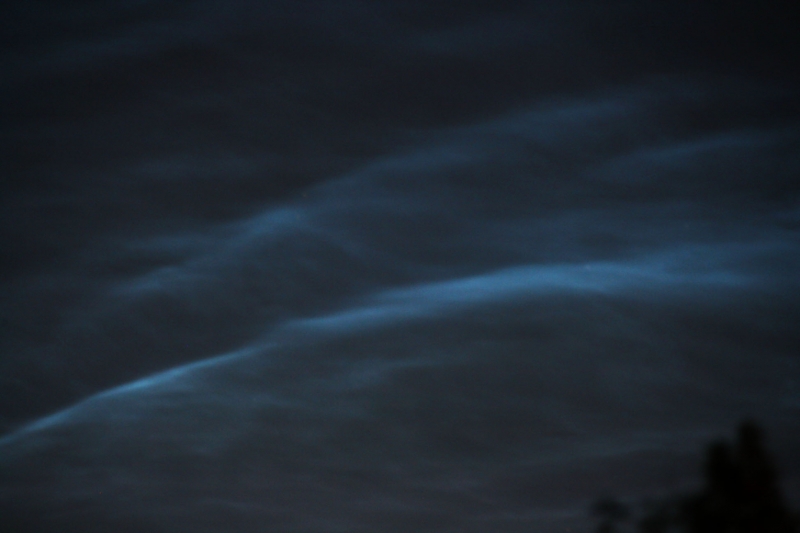
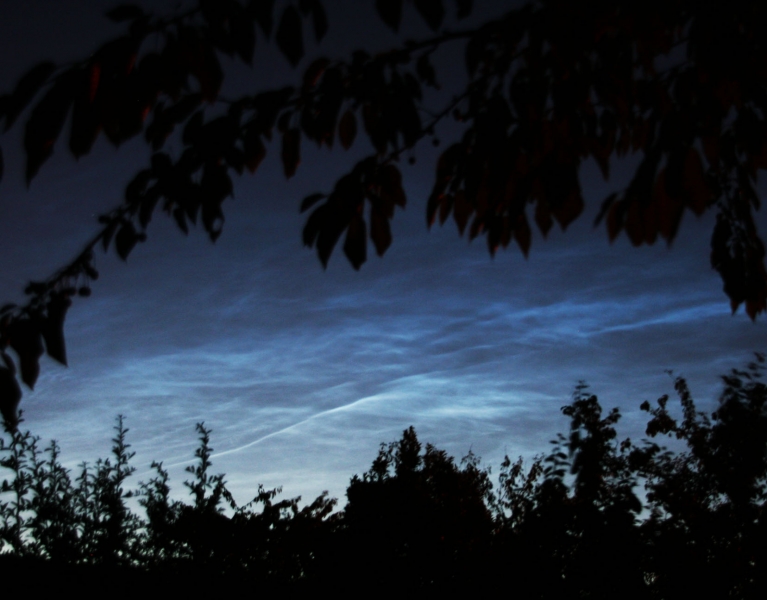
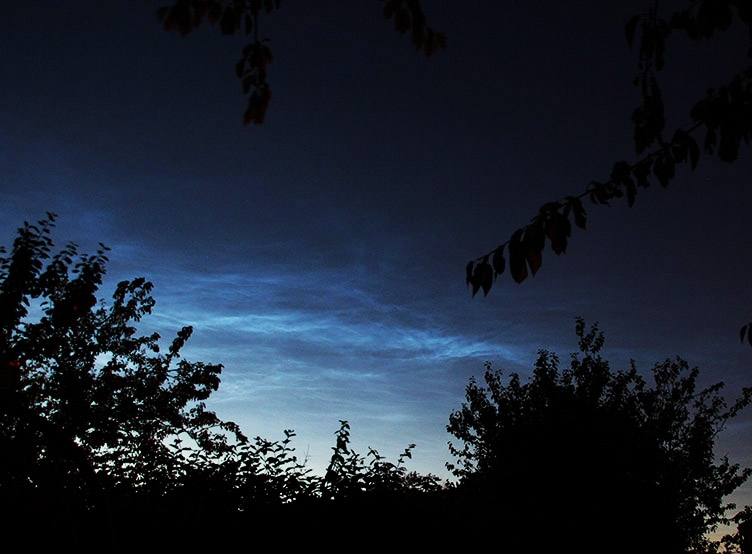
Noctilucent Cloud – 25th June 2023
Rare Noctilucent Cloud spotted by CMHASD members Diane Clarke, Martin Crow and Sonia on the 25th June 2023.
First image below was taken by Diane using a Panasonic camera DMC-TZ100, f2.8 @ 1/10sec and ISO 6400 at 11.22pm BST.

The next two images were taken by Sonia using an iPhone 8 at 11.04pm and 11.14pm BST.


The next image was taken by Martin Crow using an iPhone.

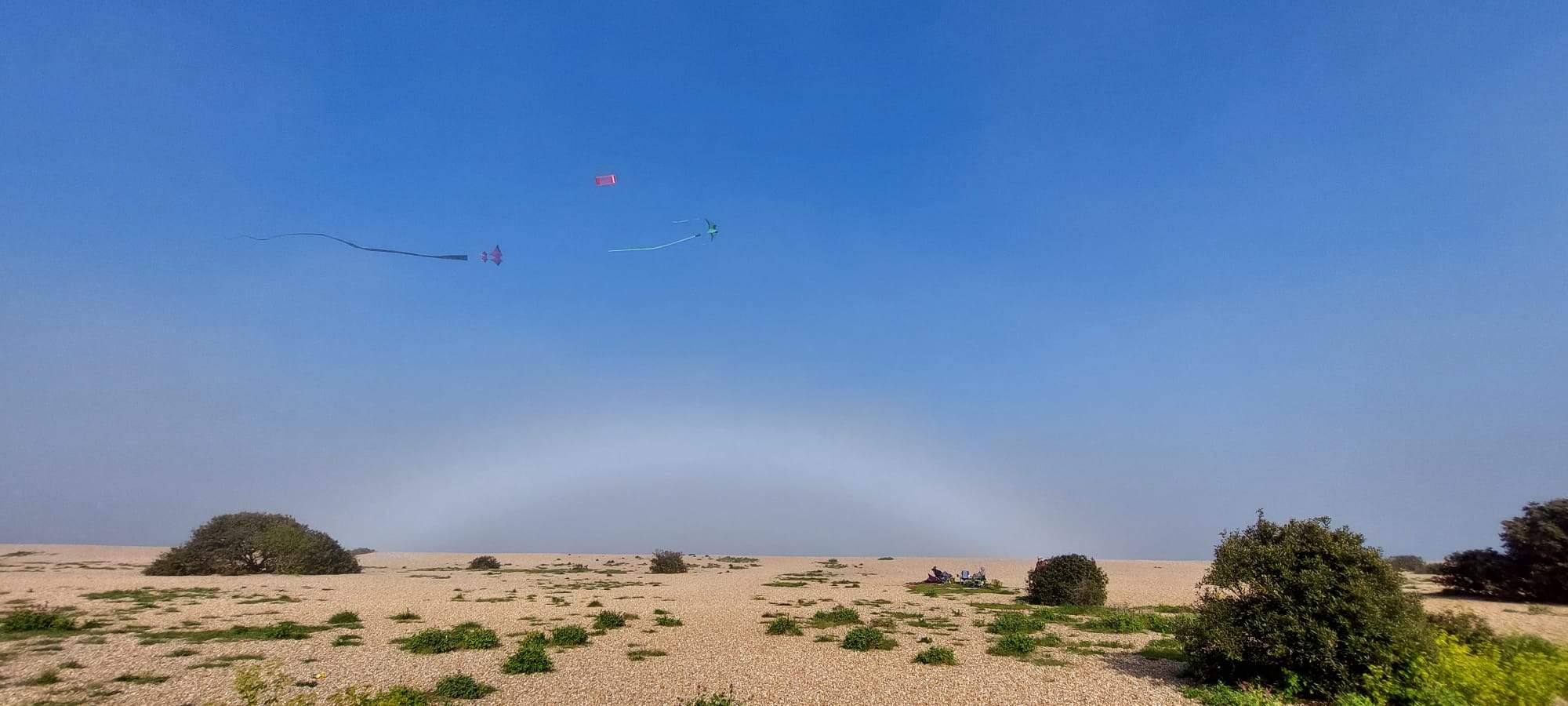
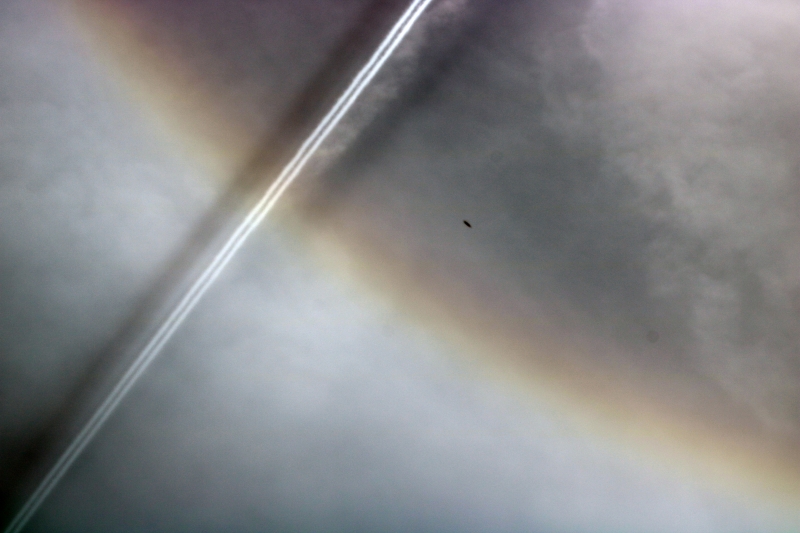
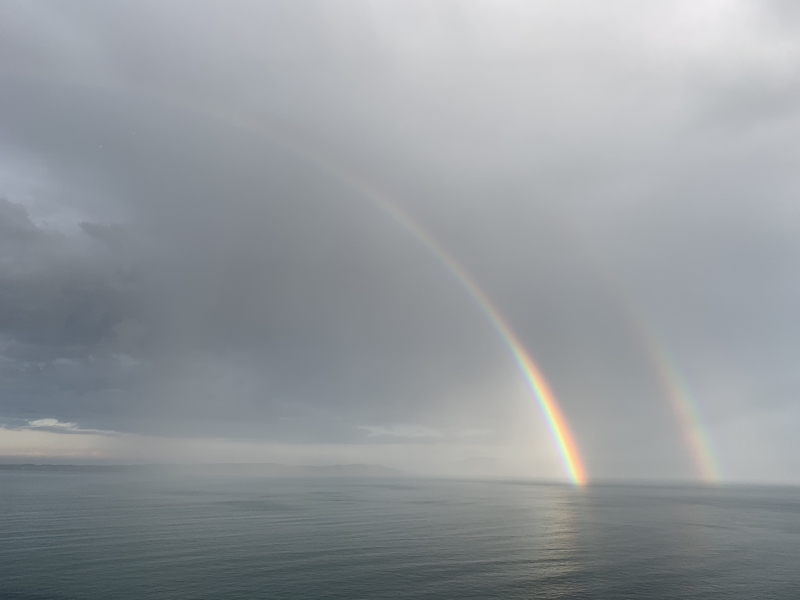
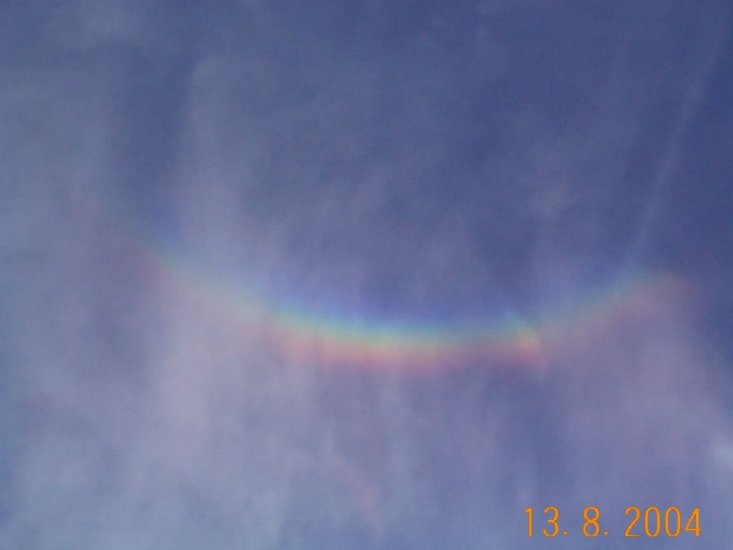
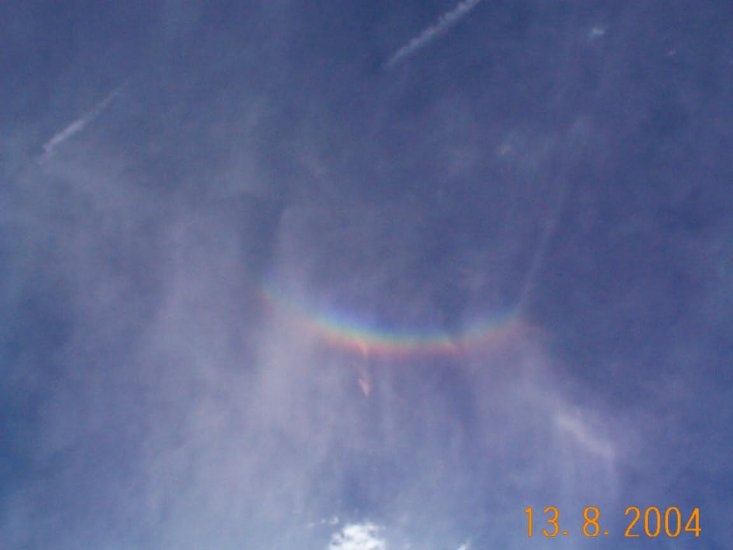
Fogbow by Kevin Smith – 7th May 2023
A great example of a fogbow captured by member Kevin Smith on the 7th May 2023.
A fogbow is a similar phenomenon to a rainbow but as its name suggests, it appears as a bow in fog rather than rain.
Due to the very small size of the water droplets that cause fog being so much smaller than in rain i.e. smaller than 0.1 mm in diameter; fogbows have very weak colours or no colour at all. Fogbows that have no colour are sometimes called ‘white rainbows’.

A Fog Bow by Kevin Smith
”How do fogbows form?
The elements that make up a fogbow are the same as for a rainbow – sunlight at the observers back, and water droplets in front. The water droplets that make up fog are so tiny compared to raindrops, between 10 and 1000 times smaller, that while the light still reflects from the water droplet back towards the observer, the process of diffraction of the light by the droplet becomes a dominant effect.
The process of diffraction broadens the reflected beam of light which smears out the colours which give the characteristic ghostly white, or very faintly coloured fogbow. This also makes the fogbow much broader than a rainbow.
The fog bank has to be relatively diffused and thin to allow the light to pass through the droplets and create the effect. Fogbows are large, almost as big as rainbows.
A similar effect can also be seen from aircraft in cloud droplets, when they’re known as cloud bows.” ref:https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/weather/learn-about/weather/optical-effects/rainbows/fogbow
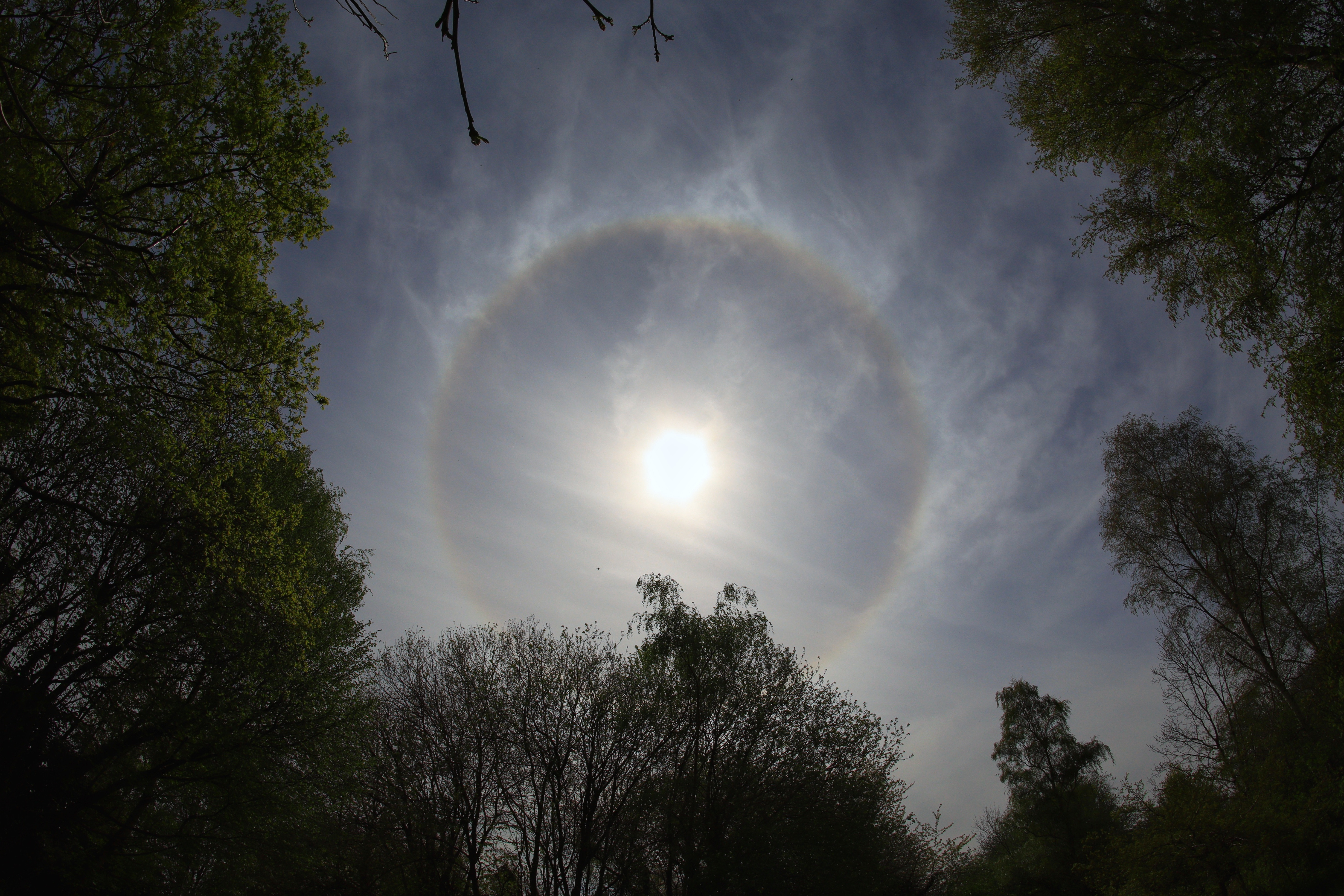
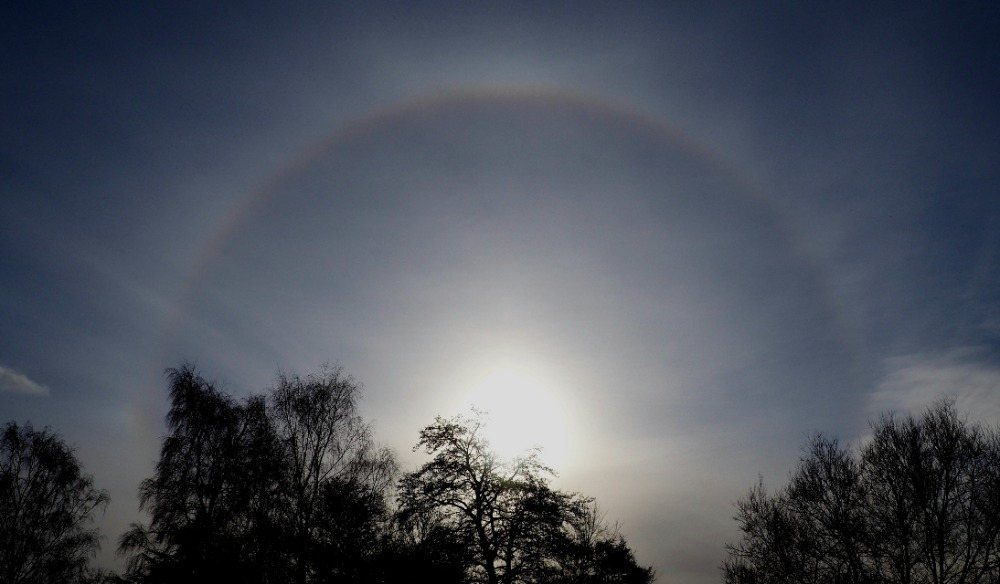
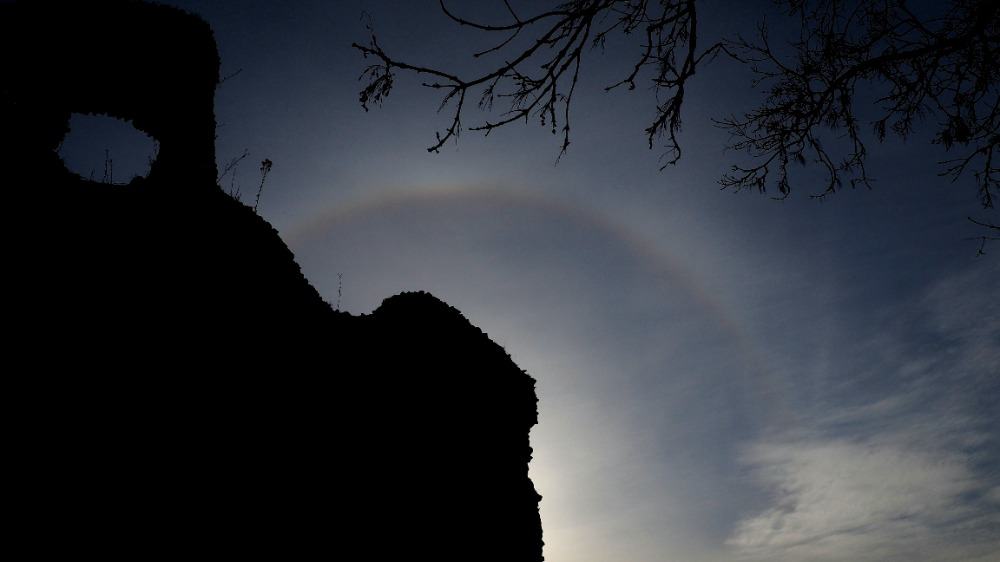
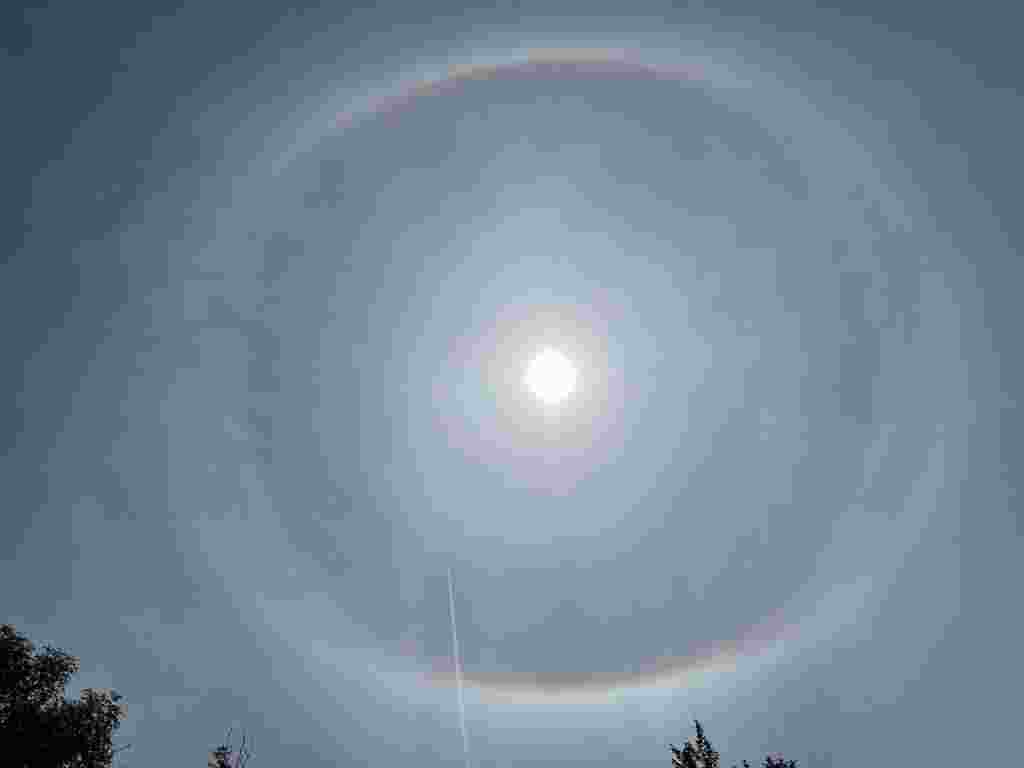
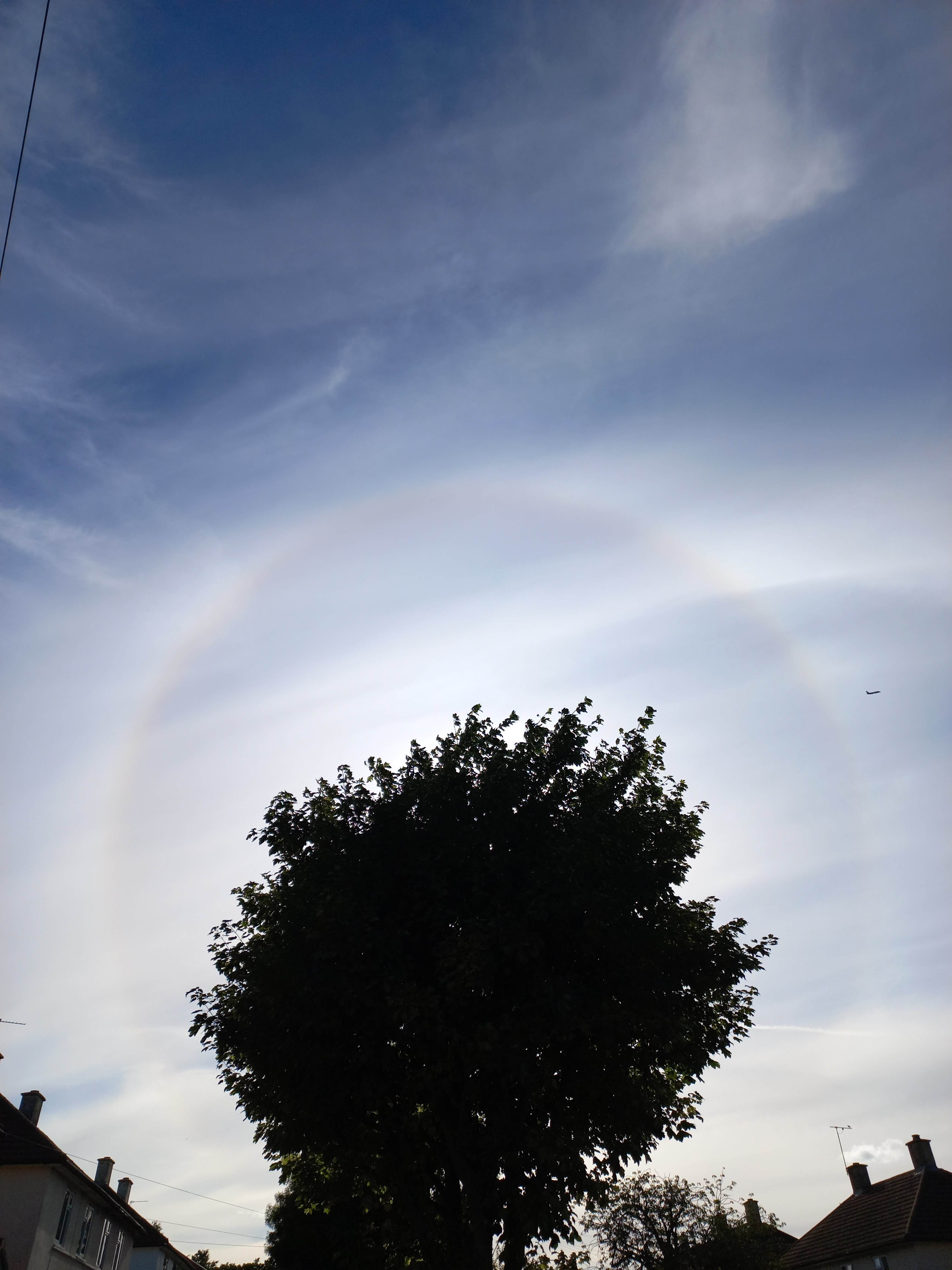
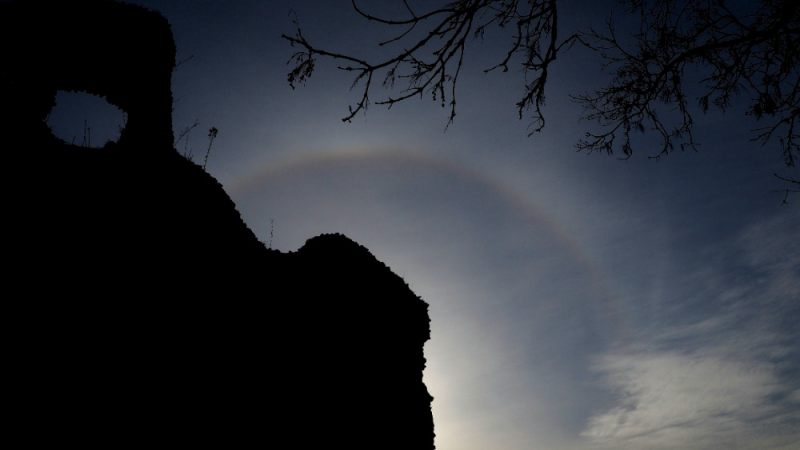
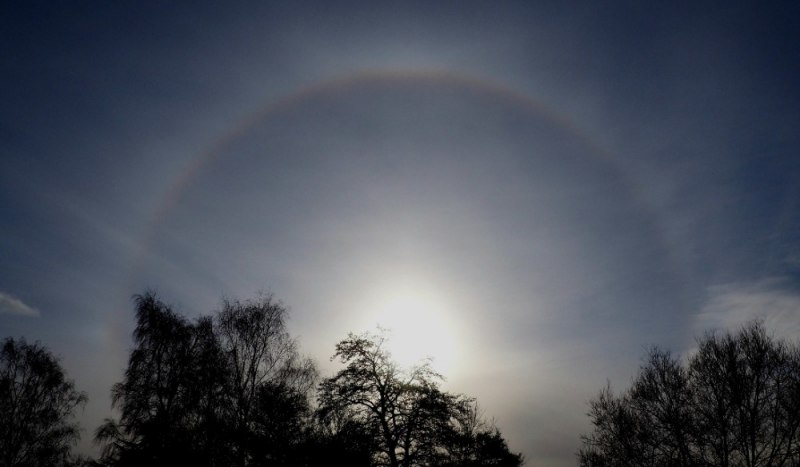
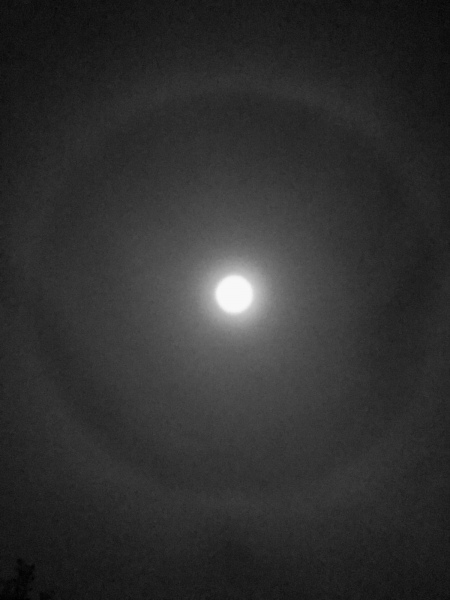
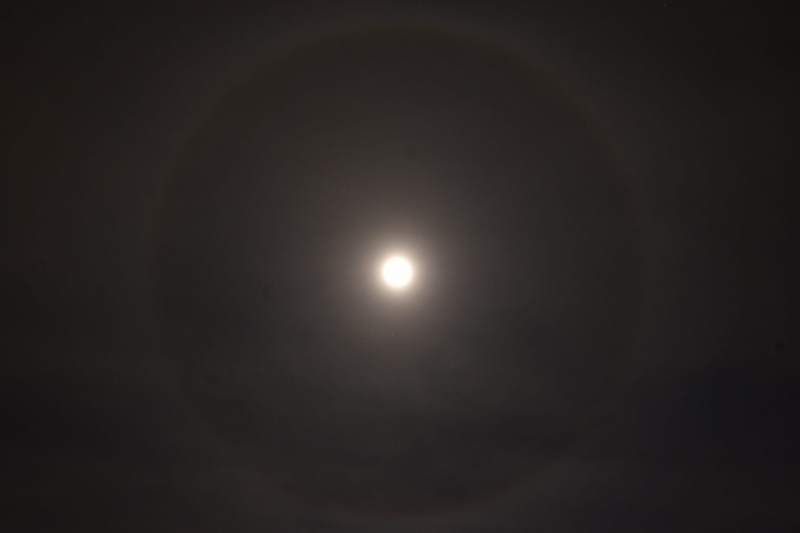
Sun Halo by John Archer – 30th April 2023
NEVER LOOK AT THE SUN DIRECTLY. Please see our Solar Observing safety page at crayfordmanorastro.com/solar-safety/
A splendid example of a Sun halo captured by CMHASD Chairman John Archer on the 30th April 2023.
A Sun halo is caused by the refraction, reflection, and dispersion of light through ice particles suspended within thin, wispy, high altitude cirrus or cirrostratus clouds.


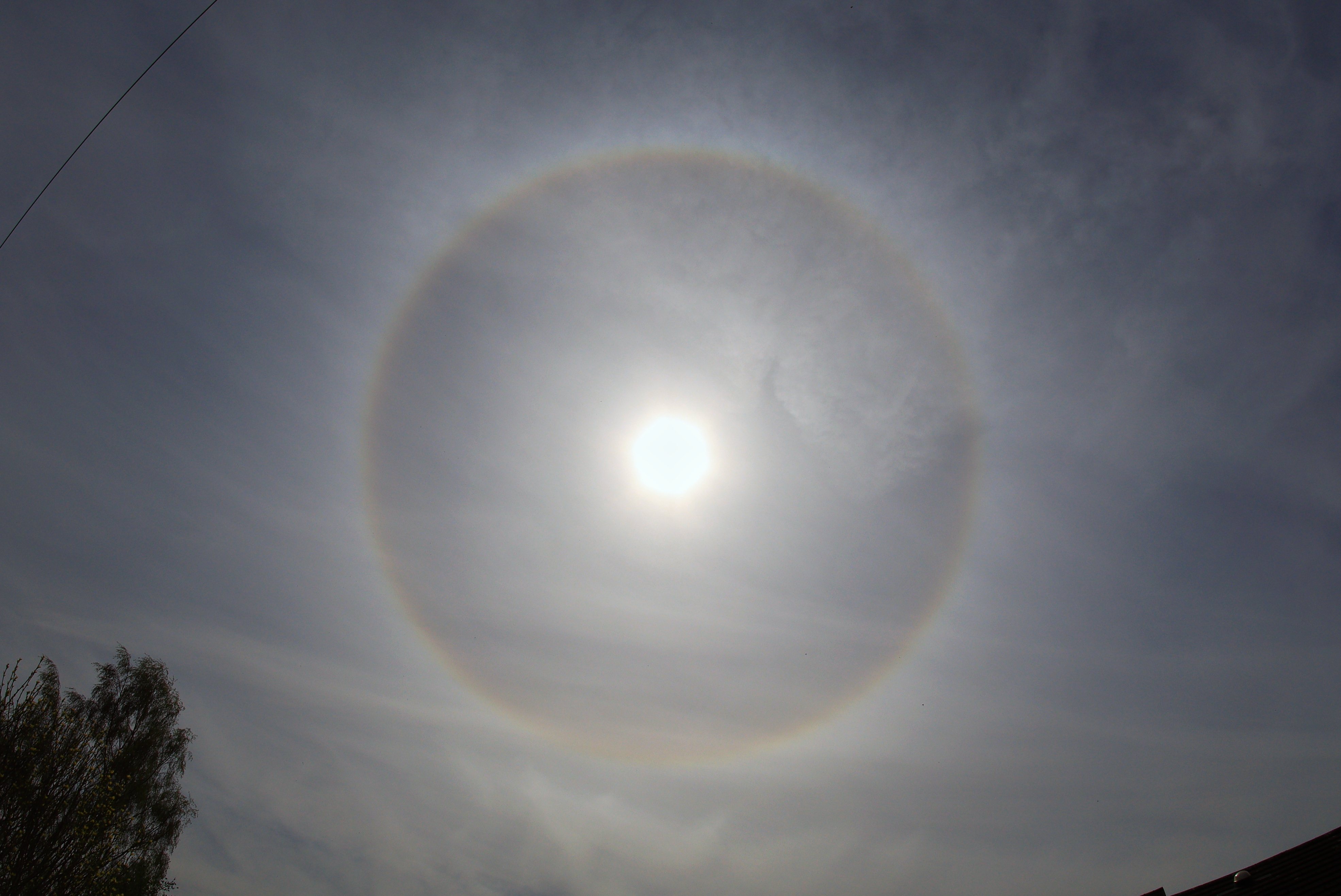
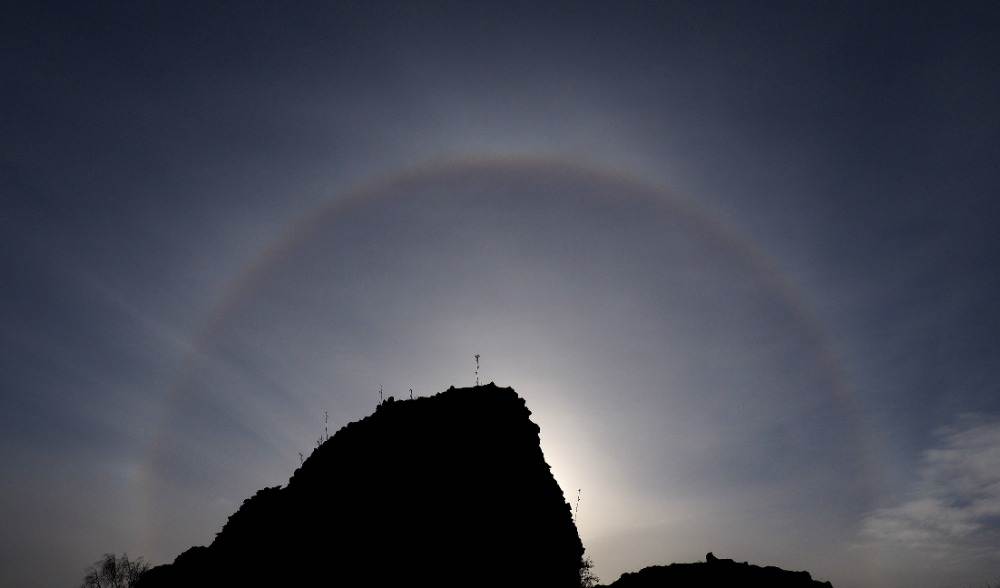
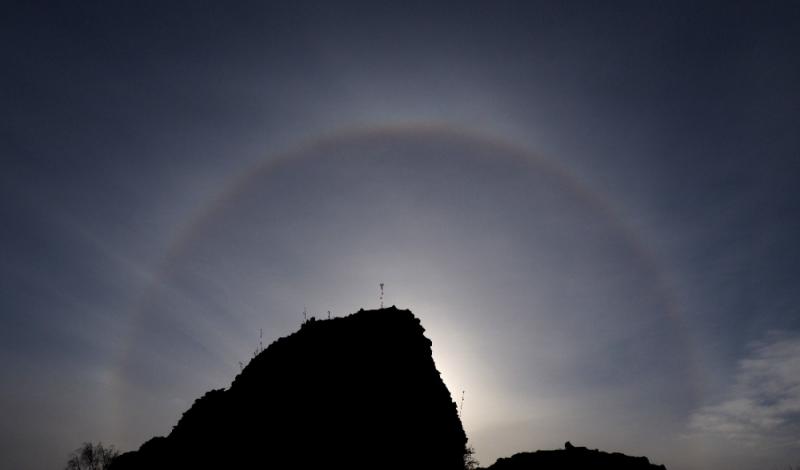
Stunning Sun Halo
CMHASD member Jim Burchell captured this superb Sun Halo on the 14th Dec 2022 around midday which lasted for quite a long time – over an hour. A Sun halo, also known as ’22 degree halo’, is an optical atmospheric phenomenon that occurs due to sunlight refracting in millions of hexagonal ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere.
More information about how Sun Halo’s are formed can be found on the Atmospheric Optics website.



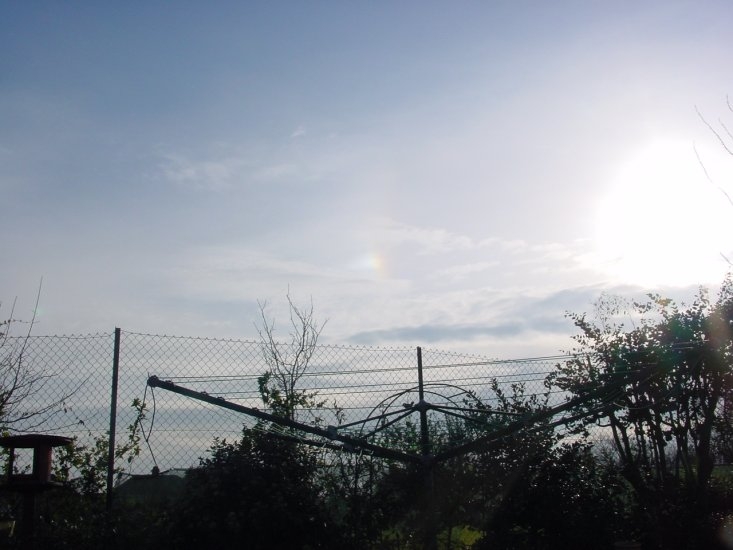
Sun dog
A shinning example of a Sundog captured by member Martin Crow when out and about on the 20th Nov 2022.
A Sundog (or sun dog) is an optical atmospheric phenomenon that causes a bright, rainbow-colored patch of light to occur on either side of the sun or both sides at an angle of 22 degrees. Sun dogs occur as a result of the refraction or scattering of light from flat hexagonal-shaped ice crystals that are suspended in clouds.
In the most brilliant displays, when 2 Sundogs appear, it’s as if there are now three suns in the sky — the main sun and two little siblings.
These “side suns” are colloquially known as sun dogs, officially known as “parhelia,” which is Greek for “next to the sun.”

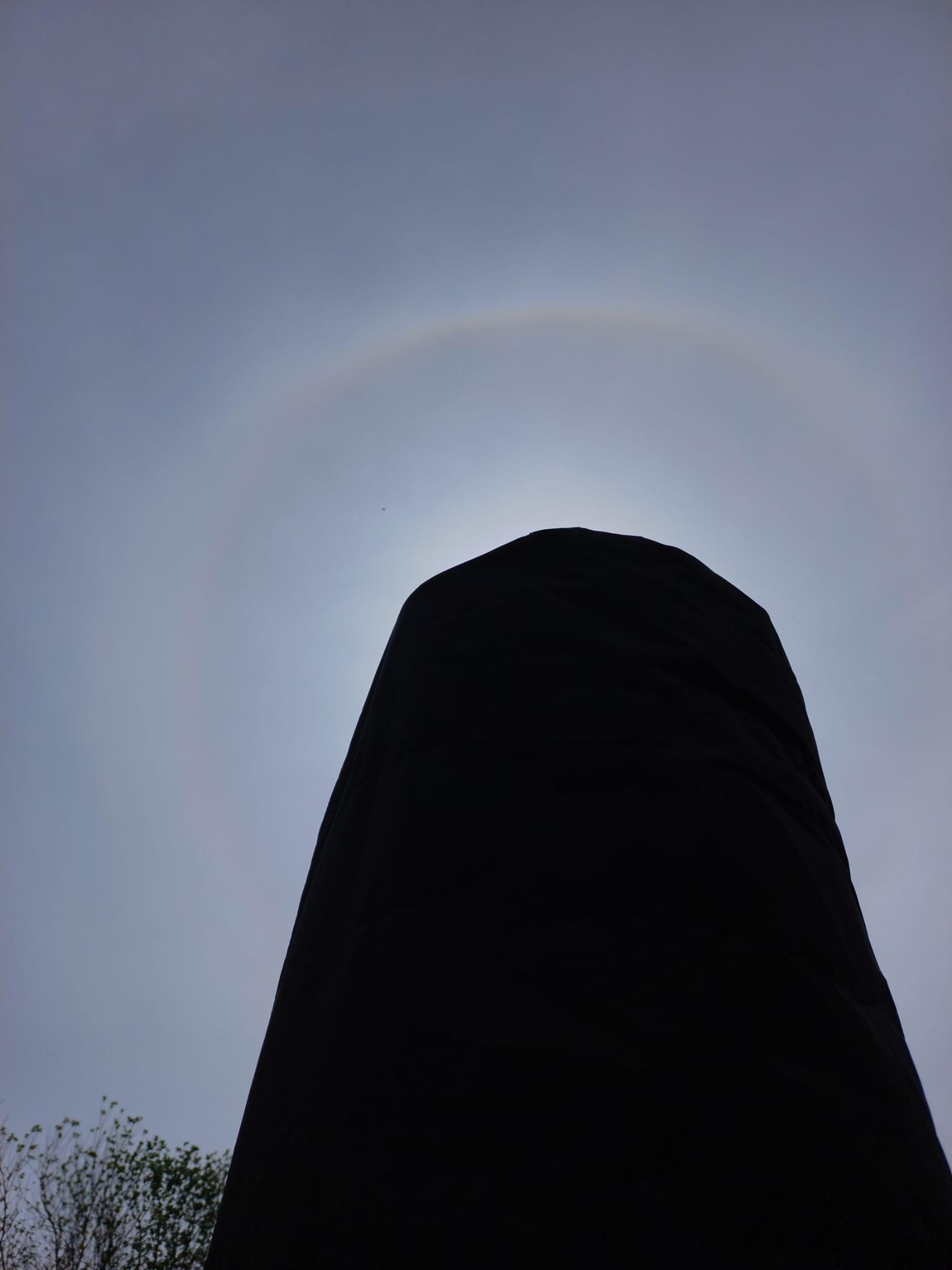
Sun Pillar by John Archer
CMHASD Chairman John Archer captured a beautiful sunrise on the morning of the 12th October 2022 along with an atmospheric phenomenon called a ‘sun pillar’ albeit a small one.
‘A sun pillar is a vertical streak of light that appears above or below a low Sun that is shining through ice-crystal clouds, such as Cirrus, Cirrostratus and Cirrocumulus, or the ground-level ice-crystal fog, diamond dust.’ https://cloudappreciationsociety.org/cloud-library/sun-pillar/
They can be 5 to 10 degrees tall and sometimes even higher. They might lengthen or brighten as you gaze at them.

Beautiful Noctilucent Cloud (NLC) spotted early morning on the 15th July 2022
OK so it is the NLC season but WOW another sighting of these rare clouds by members. A very bright & beautiful display it was too that lasted again for quite a while into dawn until 4.15am.
An alert went out at 2.33am from member Sonia as she had spotted them very low down in the North East. Two members; Diane Clarke and Jim Burchell picked up the alert and so joined Sonia in photographing the beautiful display that was to follow. All photos where taken from various locations in North Kent by the members.
Below are 4 images by Jim Burchell taken at around 3:30 am. All image’s were taken with a Pentax K70 and there has been no processing.




Below are 2 images taken by member Diane Clarke.
Panoramic view of the NLC. Diane wrote ”It went on to develop enabling me to capture 6 separate images taken at 03.30hrs that I used to create this panorama encompassing the splendour of this NLC.”

NLC at 4am as it began to fade in the North West.

Below are some images taken by Sonia using an iPhone. Also seen & photographed that morning were the planets Mars, Jupiter and Saturn, the Moon and a very curious fox who kept watch on Sonia whilst she took her photos.
NLC and the star Capella at 2.41am.

NLC developing nicely at 3.03am.

NLC at 3.10am – more finer detail emerging.

NLC at 3.21am.

NLC at 3.22am. You can see how bright they were next to a street light.

NLC at 3.38am. The NLC moved from the North East to the North West as dawn approached.

Slideshow
Other Images
Sun | Comets | Mercury | Venus | Atmospheric Optics | Meteors | Auroa and NLC | Moon | Minor Planets | Mars | Jupiter | Saturn | Uranus | Neptune | Messier | Caldwell | All Deep Sky | Conjunctions | Transits | Solar Eclipse | Lunar Eclipse | Wide Field |ISS & Space Junk | Exo-Planets
All images are copyright. Permission must be sought to from the image owner to the use of any of these images.