Observing Mars
Mars is about twice the distance from the Sun as the Earth, as a result the anguar size of Mars varies considerably depending on the relative positions of Mars and Earth in their orbits around the Sun.
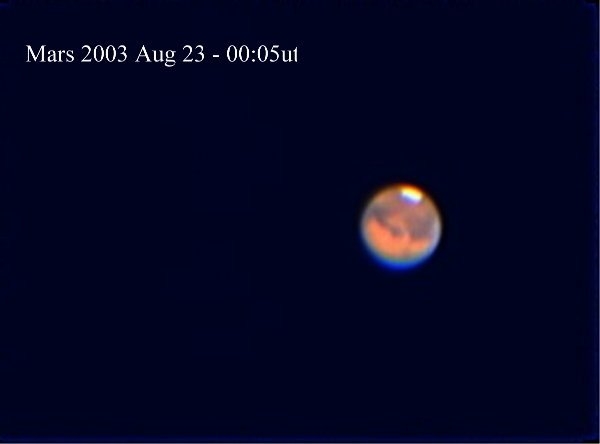
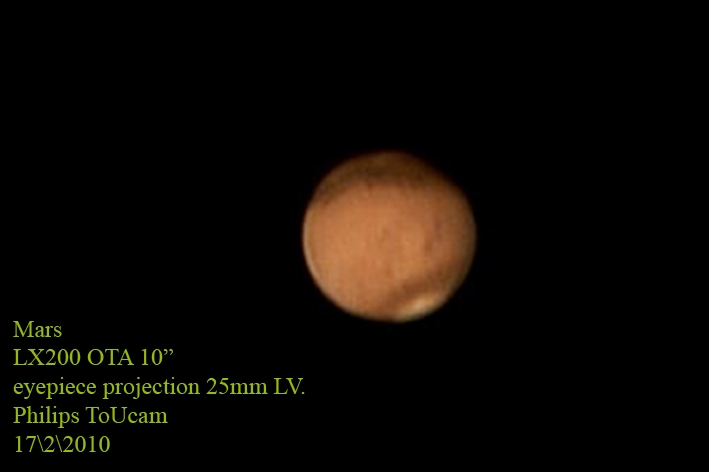
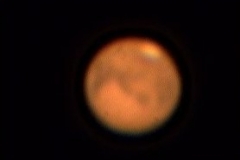
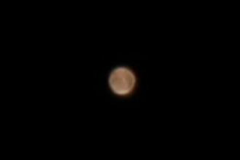
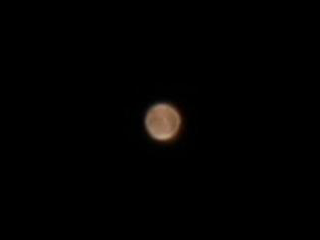
Through a small telescope you should be able to see Mars as a disk, the polar caps should also be visible and on nights with good seeing you shoudl be able to see some features on the surface.
Useful Filters:
Light Yellow (Wratten #3) Improves contract of albedo features on the surface.
Yellow-Green (Wratten #11) Good for reddish-brown surface features.
Red (Wratten #25A) Improve contrast of polar caps.
Dark Blue (Wratten 38A) Good for white clouds.
Medium Blue (Wratten 80A) Good for white clouds.
Imaging:
Lucky imaging using a digital sensor will provide the best results, a monochrome sensor will reduce your exposure time and help freeze the seeing. A red or IR Pass filter will help freeze seeing but at the expense of longer exposures.
Venus, Mars and the Twins by Simon Dawes and Jim Burchell
Two great images below of the planets Mars and Venus with the twins Castor & Pollux. Castor and Pollux are the 2 brightest stars in the constellation of Gemini.
Left to right: Mars, Pollux & Castor all nicely lined up with Venus lower right captured by member Simon Dawes on the 16th May 2023.

Below; moving again from left to right: Mars, Pollux & Castor with Venus lower right captured by member Jim Burchell on the 21st May 2023.

Sirius, Orion, Hyades in Taurus with Mars above and the Pleiades by George Buckberry
On the 17th Dec 2022 member George Buckberry captured this super image of Sirius, Orion, Hyades in Taurus with Mars above and the Pleiades. The photo was taken on a mobile Samsung SE20 in night mode and tweaked in Snapseed by George.

The Moon, Mercury, Mars & Orion by Jim Burchell
Member Jim Burchell was up early on Sunday the 9th October 2022 and took a super collection of photos of the early morning sky using his Pentax camera from Dartford. Jim captured Mercury at greatest elongation that morning; along with Mars, the Moon plus the constellation Orion.
Looking East – Mercury at greatest elongation



Looking South – the constellation Orion and Mars. Mars is above Orion (top, centre)

Looking South West – the Moon

The Moon as it set

The Pleiades, Mars and the California Nebula
In April 2019 Mars was close to M45 (the Pleiades) and NGC 1499 and this coincided with the Kelling Heath Star Party. Unfortunately at this time of year Taurus is very low, setting in the late evening making this a difficult object to image, my attempts to stack and then process with Deep Sky Stacker were hopeless, so I turned to Astro Pixel Processor (using a 30 day free trial) which has a very easy to use light pollution killer, this allowed me to remove the gradient that resulted from the very low elevation and trees that crept into the field.
Total exposure is 84 minutes, from 30s subs. Tracking was achieved with an iOptron Star tracker, camera was a Canon 600D with a full spectrum mod and a CLSCCD clip-in filter.
Martin Crow’s Images of Mars
Simon Dawes’ Images of Mars
Julian Tworek’s Images of Mars
Honor Wheelers Images of Mars
Gordon Collins Images of Mars
Slideshow
Other Images
Sun | Comets | Mercury | Venus | Atmospheric Optics | Meteors | Auroa and NLC | Moon | Minor Planets | Mars | Jupiter | Saturn | Uranus | Neptune | Messier | Caldwell | All Deep Sky | Conjunctions | Transits | Solar Eclipse | Lunar Eclipse | Wide Field |ISS & Space Junk | Exo-Planets
All images are copyright. Permission must be sought to from the image owner to the use of any of these images.