[et_pb_section fb_built="1" _builder_version="4.7.4" _module_preset="default" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_row _builder_version="4.7.4" _module_preset="default" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_column type="4_4" _builder_version="4.7.4" _module_preset="default" global_colors_info="{}"][et_pb_text _builder_version="4.7.4" _module_preset="default" global_colors_info="{}"]
Members Simon Dawes and Martin Crow have been named as contributors on a scientific paper published this week, Martin and Simon along with other amateur and professional astronomers have been observing exo-planet transits - each observation takes between 4 and 5 hours typically so is quite a commitment. Well done Mrtin and Simon and all the other amateur astronomers who submitted observations.
Abstract
The Ariel mission will observe spectroscopically around 1000 exoplanets to further characterise their atmospheres. For the mission to be as efficient as possible, a good knowledge of the planets' ephemerides is needed before its launch in 2028. While ephemerides for some planets are being refined on a per-case basis, an organised effort to collectively verify or update them when necessary does not exist. In this study, we introduce the ExoClock project, an open, integrated and interactive platform with the purpose of producing a confirmed list of ephemerides for the planets that will be observed by Ariel. The project has been developed in a manner to make the best use of all available resources: observations reported in the literature, observations from space instruments and, mainly, observations from ground-based telescopes, including both professional and amateur observatories. To facilitate inexperienced observers and at the same time achieve homogeneity in the results, we created data collection and validation protocols, educational material and easy to use interfaces, open to everyone. ExoClock was launched in September 2019 and now counts over 140 participants from more than 15 countries around the world. In this release, we report the results of observations obtained until the 15h of April 2020 for 119 Ariel candidate targets. In total, 632 observations were used to either verify or update the ephemerides of 83 planets. Additionally, we developed the Exoplanet Characterisation Catalogue (ECC), a catalogue built in a consistent way to assist the ephemeris refinement process. So far, the collaborative open framework of the ExoClock project has proven to be highly efficient in coordinating scientific efforts involving diverse audiences. Therefore, we believe that it is a paradigm that can be applied in the future for other research purposes, too.
Full article is available here
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]

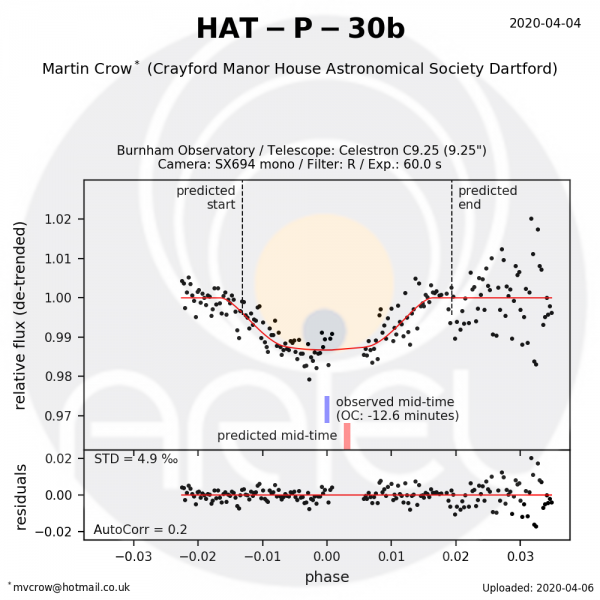
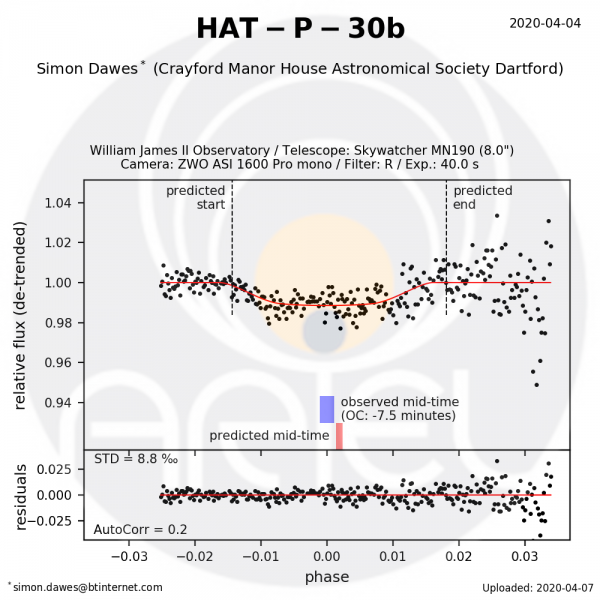
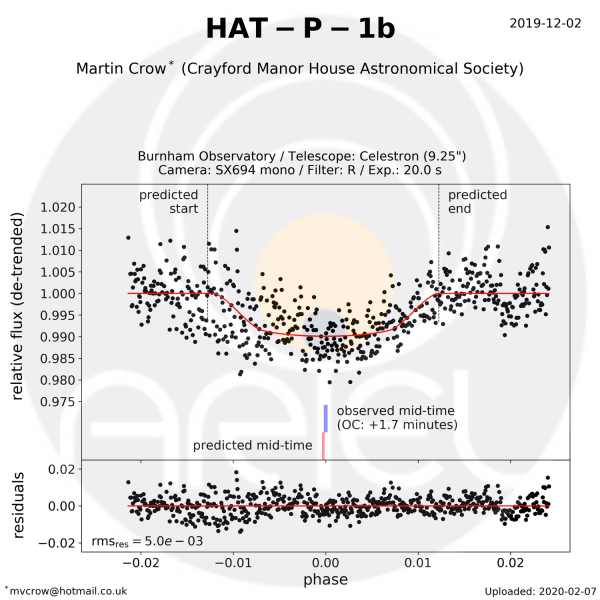
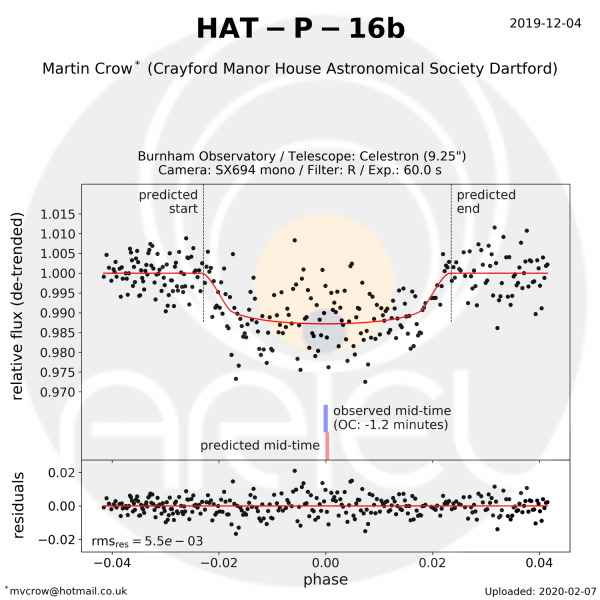
 Observation by Martin Crow for the EXC-Clock project[/caption]
Observation by Martin Crow for the EXC-Clock project[/caption]